What is an ecommerce business plan?
An e-commerce business plan is a document that outlines your business and its goals, analyzes your industry and competitors, and identifies the resources needed to execute your plan. It also lists the e-commerce retailers you’ll use to distribute your products and the marketing strategies you’ll use to drive sales.
Here’s a helpful guide to starting an ecommerce business. Whether a company operates as a startup or has years of operations and growth under its belt, an ecommerce business plan is essential for evaluating a business and determining areas of improvement.
An ecommerce business plan is vital for increasing numbers of shoppers conducting business online. It's estimated that the number of ecommerce users in the US alone will grow to 333.5 million by 2029. An ecommerce business plan keeps you organized and is useful when seeking investors who need to understand your company.
Components of an Ecommerce Business Plan
While the different sections of an ecommerce business plan are tailored to the needs of a particular organization, below are some standard components.
Cover Page
Keep the cover page simple and professional. A cover page should typically include the following:
- Company name.
- Logo.
- Contact information of the founder.
- Company address.
- One-line description of the company.
Executive Summary
An executive summary, like the name suggests, is a summary of what the ecommerce business plan will cover. Later in the article, I discuss what an executive summary should include in more detail.
Company Summary and Opportunity
This section generally contains a company synopsis, a short description of the products and services, a brief history of the business, the mission statement, and the team and management structure. It should also cover the challenges the business solves and how it aims to do so.
Target Market and Audience
In this section, describe the state of the current industry, major trends, and key competitor details. Additionally, talk about what your target customer(s) and buyer persona(s) look like (along with demographics, psychographics, and pain points) and also why they’d be interested in your product or service.
Product and Services
This section should detail the products and service lines along with the pricing strategy to be used.
Marketing and Sales Plan
Marketing and sales are vital to a business’ success, so it’s essential to list the methods to be employed. The image below includes the key aspects to include in this section. I also elaborate more on what a marketing plan and sales plan should cover later in this piece.
Financial Plan
This section covers monetary details. Topics to cover include costs, revenue streams, projected revenue, and funding requirements and sources.
Goal Planning
This section notes down goals and milestones to be achieved, particularly in the first year. “What will success look like?” — that’s the question to be answered here. It’s even better if certain goals can be data, number, or metric-based.
How to Write an Ecommerce Business Plan
1. Give an executive summary.
- An executive summary is a one-to-two-page overview of your business. The purpose of an executive summary is to let stakeholders know what the business plan will contain.
- It's important to provide an executive summary. This allows investors or executives who don’t have the time to read your full plan to quickly see the most important highlights.
2. List and describe your business.
This is the section that needs the most detail because it highlights what you're selling. To begin, I’d provide an overview of your product or service. For instance, a photography company would probably list their photo packages arranged by price and services
3. Detail your products and services.
Once I have described my business and its purpose, I’m ready to dive deeper into the plan. What products and services do I or will I offer?
This is an opportunity to list each item and its purpose, allowing me to answer the question, “Why?” In other words, why am I choosing to offer these specific products and services?
After detailing my products and services, I’d outline the pricing model. What is the cost associated with each service? What will the profit margin look like? Determining price, especially as a startup, can be challenging. However, sales pricing calculators can help determine the best pricing strategy.
4. Conduct a market analysis.
For the market analysis, I’d provide the operational climate of the industry I’m in. To illustrate, at this step, the photography company would need to analyze its position in a world of rival companies like Adobe or online services like Canva.
Driving & Enhance E-Commerce Forward with Odoo 17 AI-Powered
AI-Powered Ecommerce Elevating Customer Experiences, Optimizing Operations: A Comprehensive Guide by an Ecommerce Expert
5. Strategize your marketing plan.
Having the right marketing plan for your ecommerce business is crucial for any business. It serves as a roadmap for how your company will build brand awareness, reach your target audience, and boost sales and revenue.
As seen in this template, your marketing plan will focus on positioning strategy, acquisition channels, and tools and technology.
I’ll take a look at each one:
- Positioning strategy. This fixates on how you will position yourself to your audience. How will you address their challenges and goals? How will you use the tools at your disposal to accomplish this?
- Acquisition channels. The marketing plan will also require you to focus on where your customers come from. Are they finding your business through search engine marketing? Do they discover your business from your blog or social media accounts? Identifying your acquisition channels allows you to identify which ones to prioritize.
- Tools and technology. Lastly, your marketing plan should lay out the tools and technology your marketing team will need and use. Will you use a content management system (CMS)
6. Create a sales plan.
When creating a sales plan, I’d describe the methodology, organization structure, sales channels, and technology.
For example, when discussing methodology, will I focus on an inbound strategy where I attract customers to my business through my content or an outbound strategy where I initiate contact with my prospects? And what’s the reason behind this decision?
This part of the ecommerce business plan will also require me to outline the people in charge of selling my products and services, as well as what channels they’ll use to sell the products.
Similar to creating the marketing plan, the sales plan will also require a brief on what tools I plan to use.
7. Outline legal notes and financial considerations.
In the following two sections of your business plan, I’d describe the legal and financial structures.
For example, the photography company should provide details on the legal considerations like online safety rules, ecommerce regulations, and the company's costs.
Legality and finances are crucial information for investors and stakeholders. In this section, it's important to be honest and thorough to give partners a realistic idea of how to contribute.
Ecommerce Business Plan Tips
Before you lay out the business plan and set the tone for your ecommerce business, there are some factors that are essential to consider. These factors lay the foundation of your business and will help you construct the document with ease.
I’ve noted down some of the most crucial business plan tips and tricks:
Find the purpose of your plan.
There is not merely one purpose behind writing the business plan. Different business plans serve different purposes for ecommerce owners.
There are three main purposes of a business plan:
- Gain secured financial support. Ecommerce businesses are in dire need of investors, and hence, their business plan with all the objectives, competitor analysis, frameworks, and supporting documents use this to gain financial support.
- To set the direction for your teams. Businesses include metrics like target market, pricing comparison, working process, objectives, and other nitty-gritty in their plans to help their teams align and achieve the desired results.
- Attract relevant customers. With the current markets and trends in a well-laid business plan, it becomes easier to determine the segment of your target audience.
Driving & Enhance E-Commerce Forward with Odoo 17 AI-Powered
Driving & Enhance E-Commerce Forward with Odoo 17 AI-Powered course is the ultimate resource for professionals who want to understand and utilize AI’s transformative potential. It is the blueprint for understanding and applying AI, giving your business just the edge you’ve been waiting for.

Artificial Intelligence in Ecommerce: How This Rapidly Evolving Tech Will Change the Online Storefront
E-COMMERCE
Odoo 18 easily connects with other company modules and provides a complete eCommerce management solution. Odoo 18 gives companies an all-in-one platform for effectively managing their online sales operations with capabilities including order processing, product catalog management, and website construction.
A new menu called Shop will appear on the page when the eCommerce module has been installed. From there, customers can easily buy products.
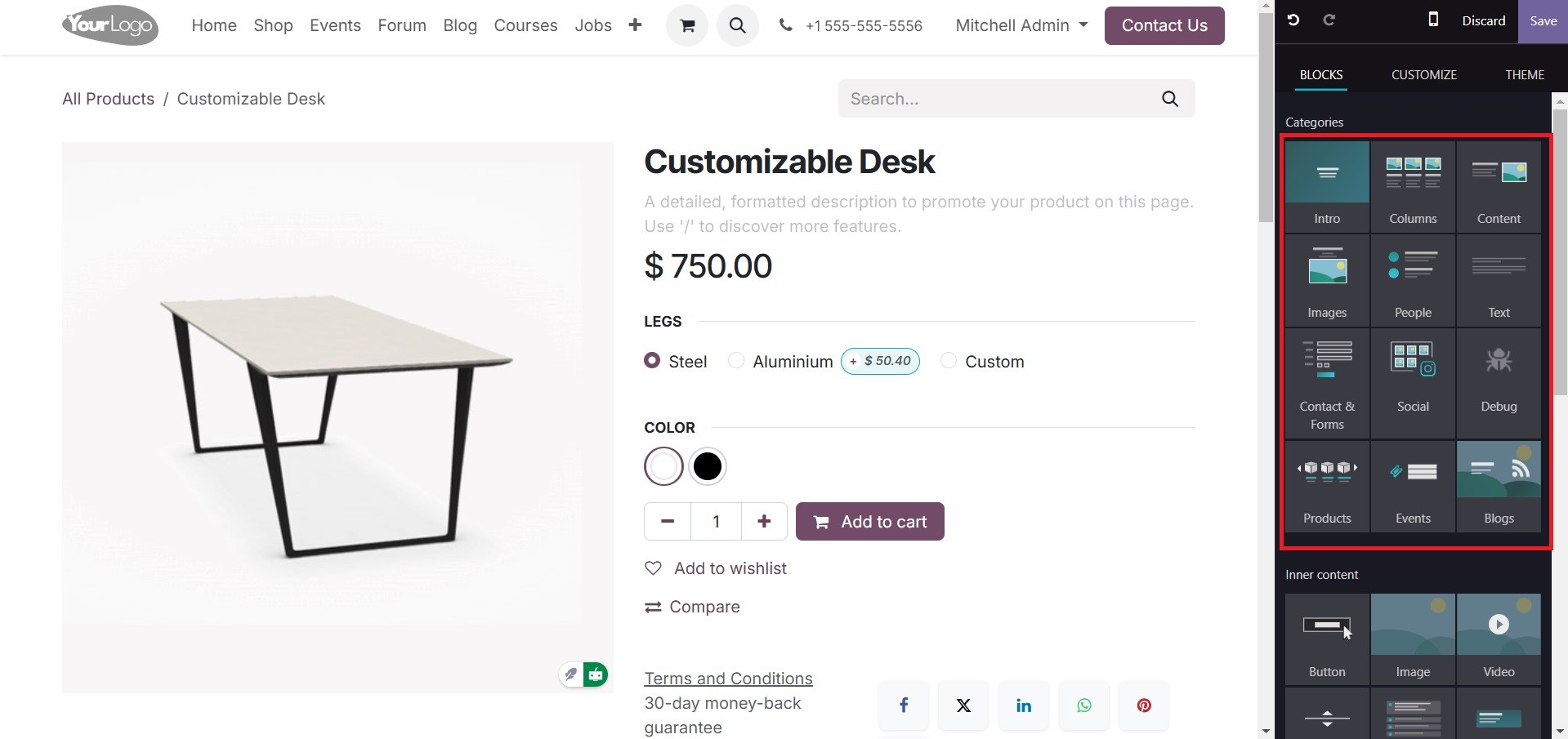
Users can improve the functionality and user-friendliness of the page with the Odoo 18 website builder. Customers can also utilize the Rating option which is user-friendly and enables the installation of certain themes, as shown below, to contribute ratings to our page.
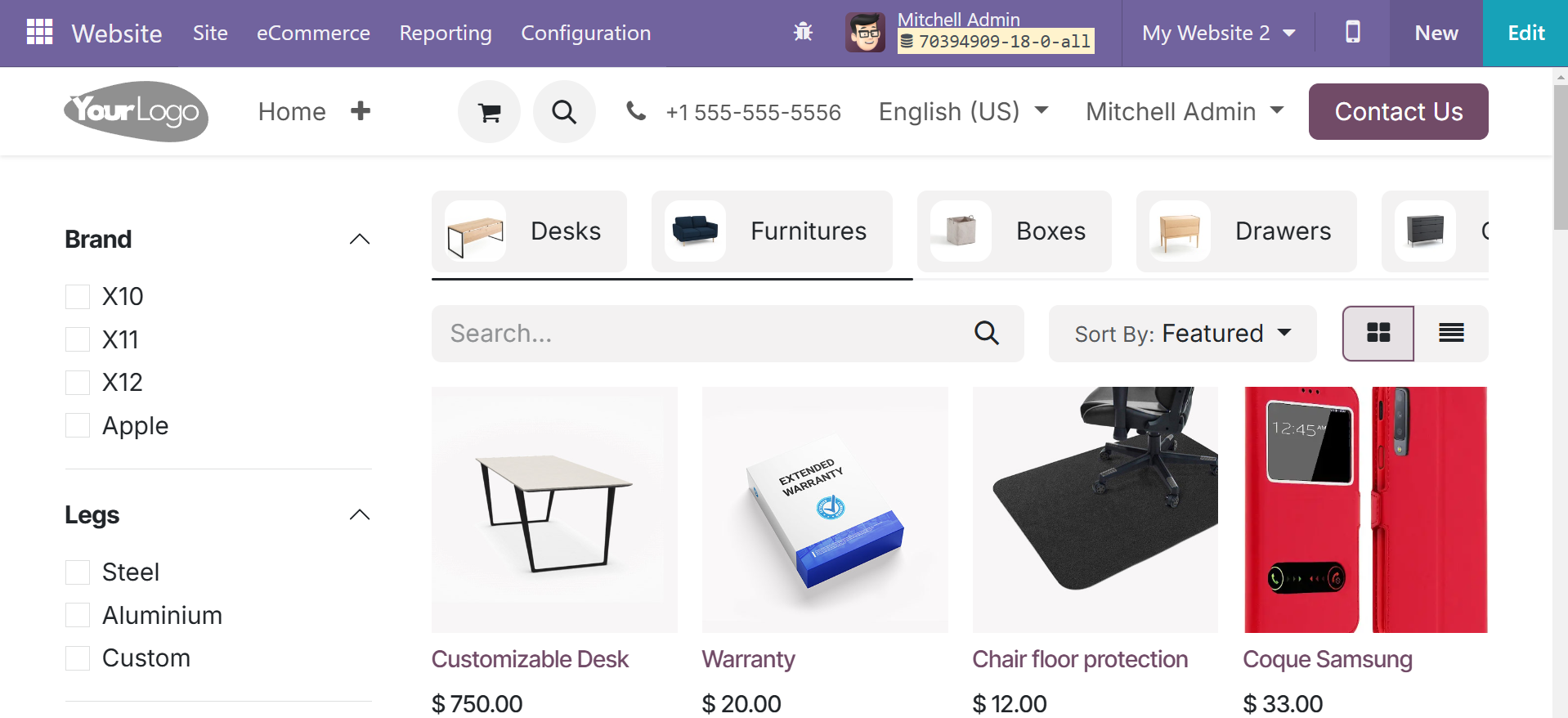
There are different blocks, such as intro, column, content, image, people, text, contact and form, social debug, product, event, and blogs, as in the below screenshot.
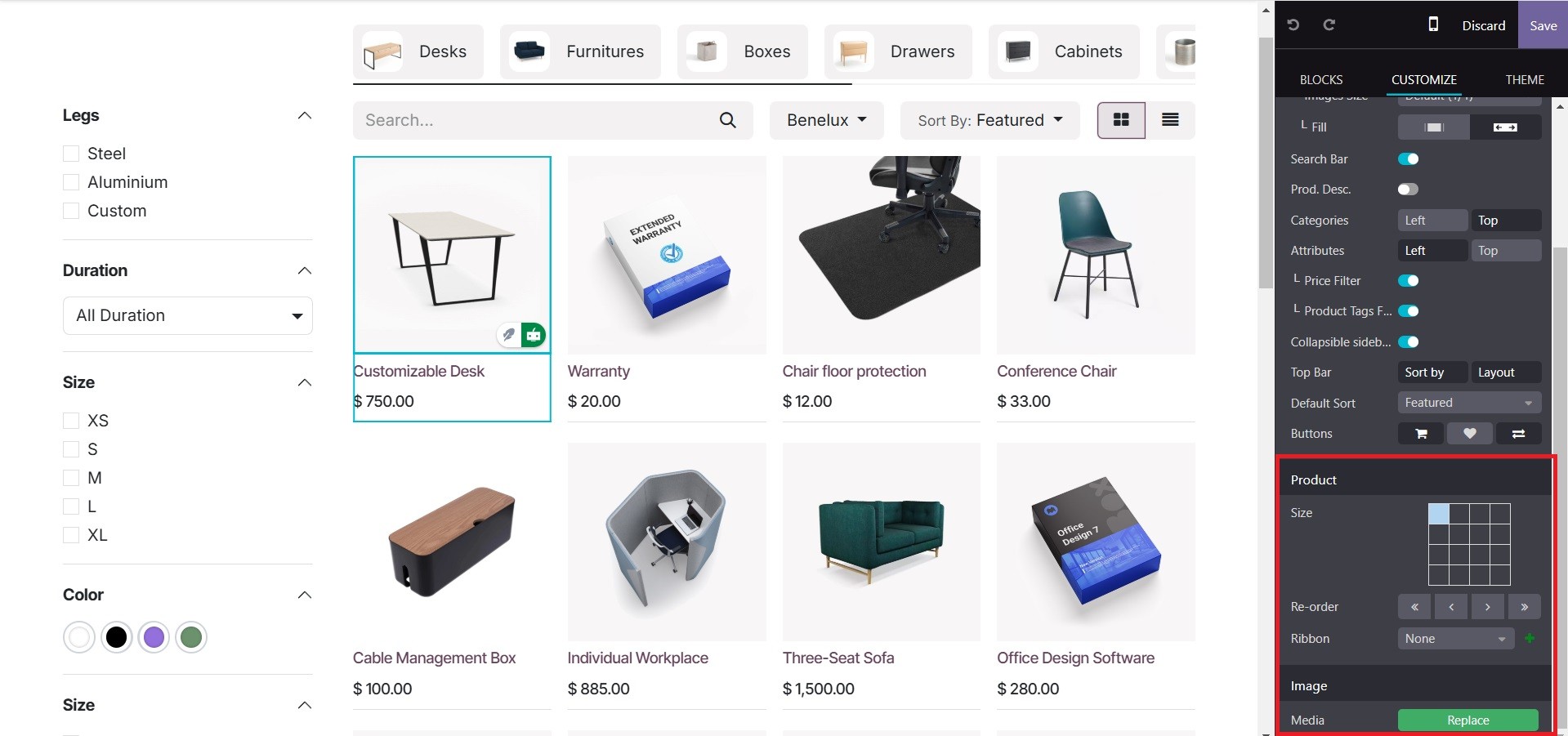
The user can alter any element of the product on several pages with Odoo 18. When we choose a product on the store page and choose the edit option, for instance, we are shown a variety of characteristics unique to product pages, such as layout, which contains a grid and options list, size, style, and a top bar, among many other features. A special area for product customisation is also available, with choices for badges, photos, reordering, and size.
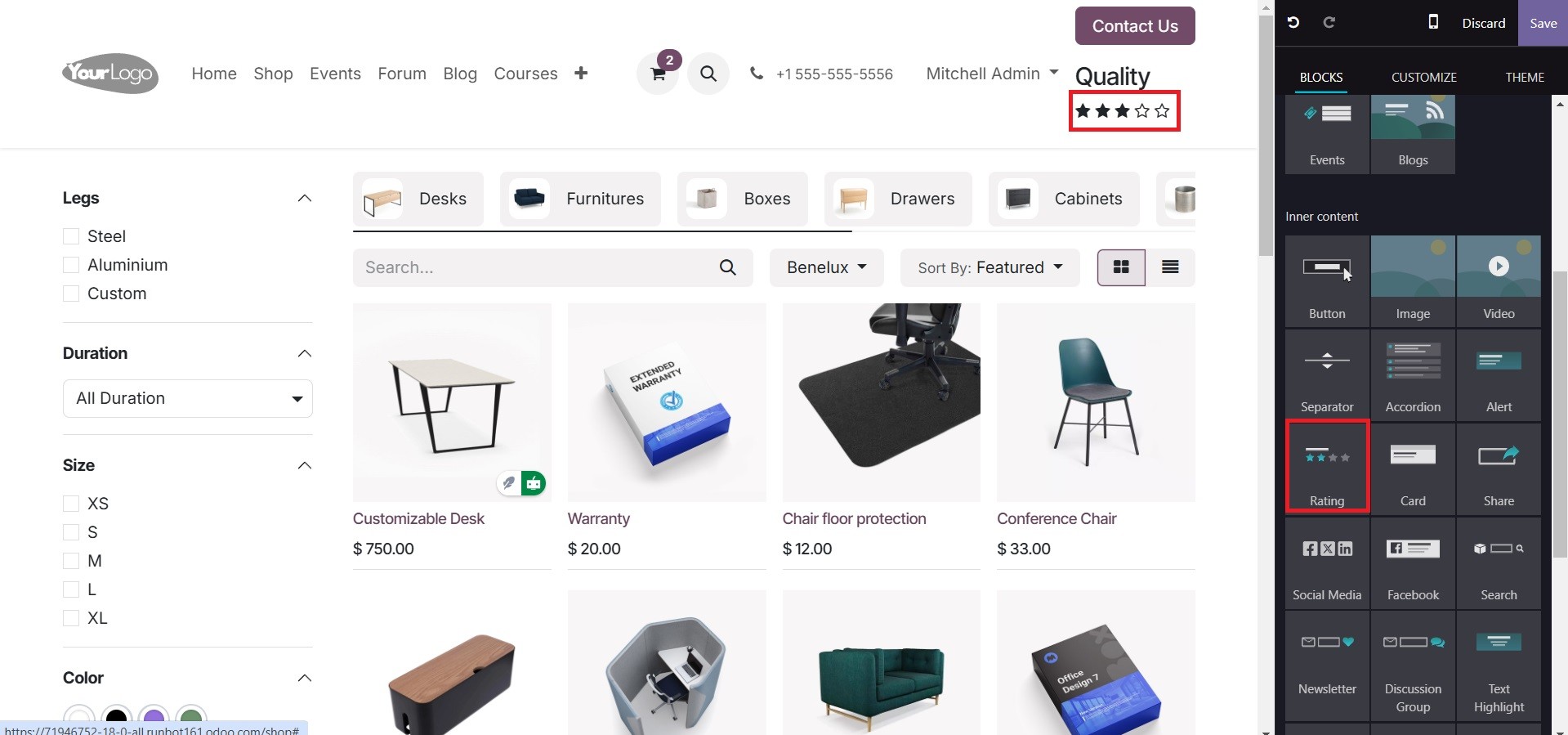
As seen below, the user can also include buttons like Add to Cart, Wishlist and Compare to make it simpler for customers to access.
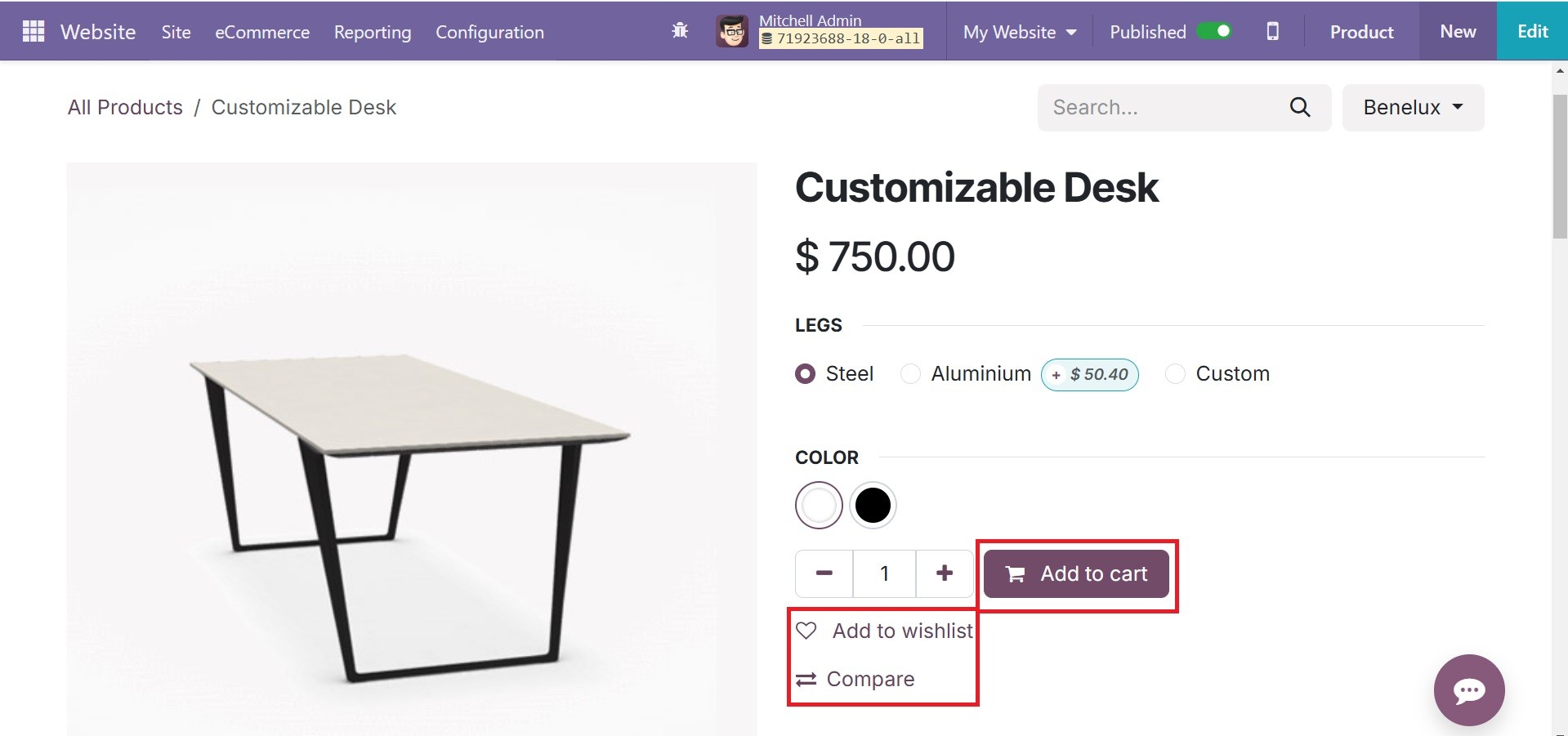
Furthermore, the customer can upload additional photographs from the product's customization page, as shown below. Customers may more easily ascertain if a product is tax-included or excluded with Odoo 18's tax indicator functionality.
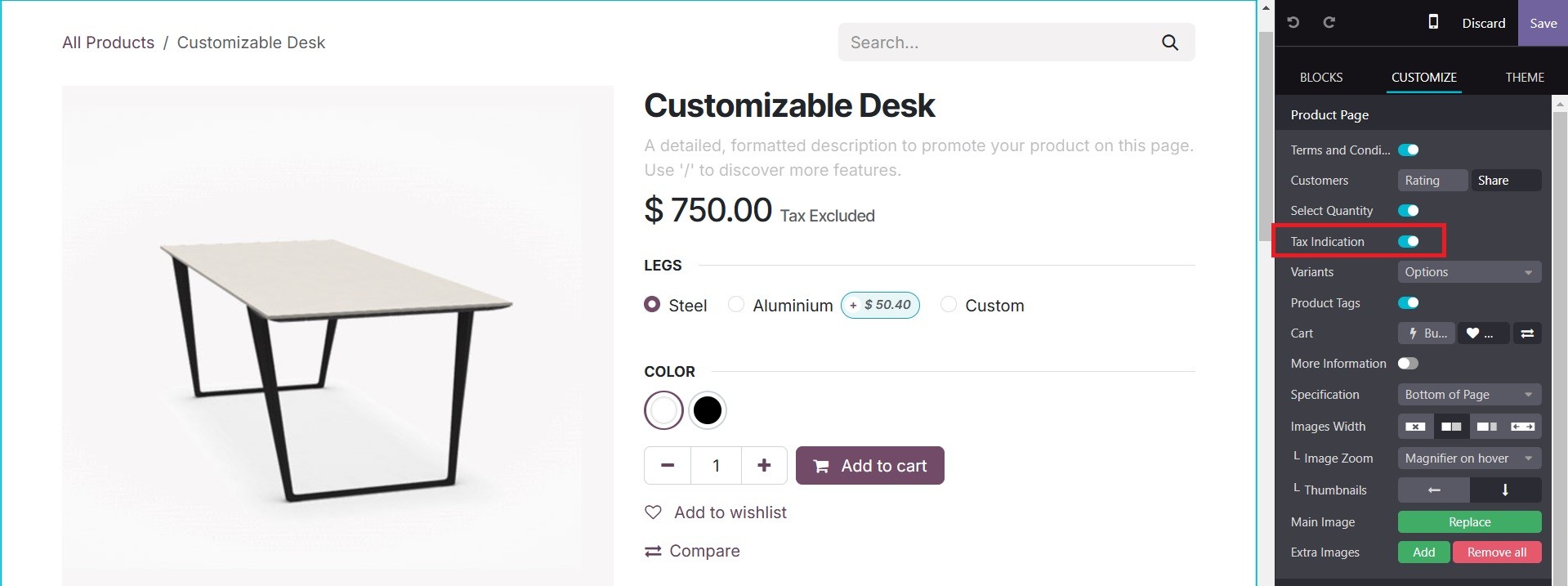
The customer can additionally add many photographs to the product by selecting the "Extra Images" option on the product form that is situated beneath the sales page.
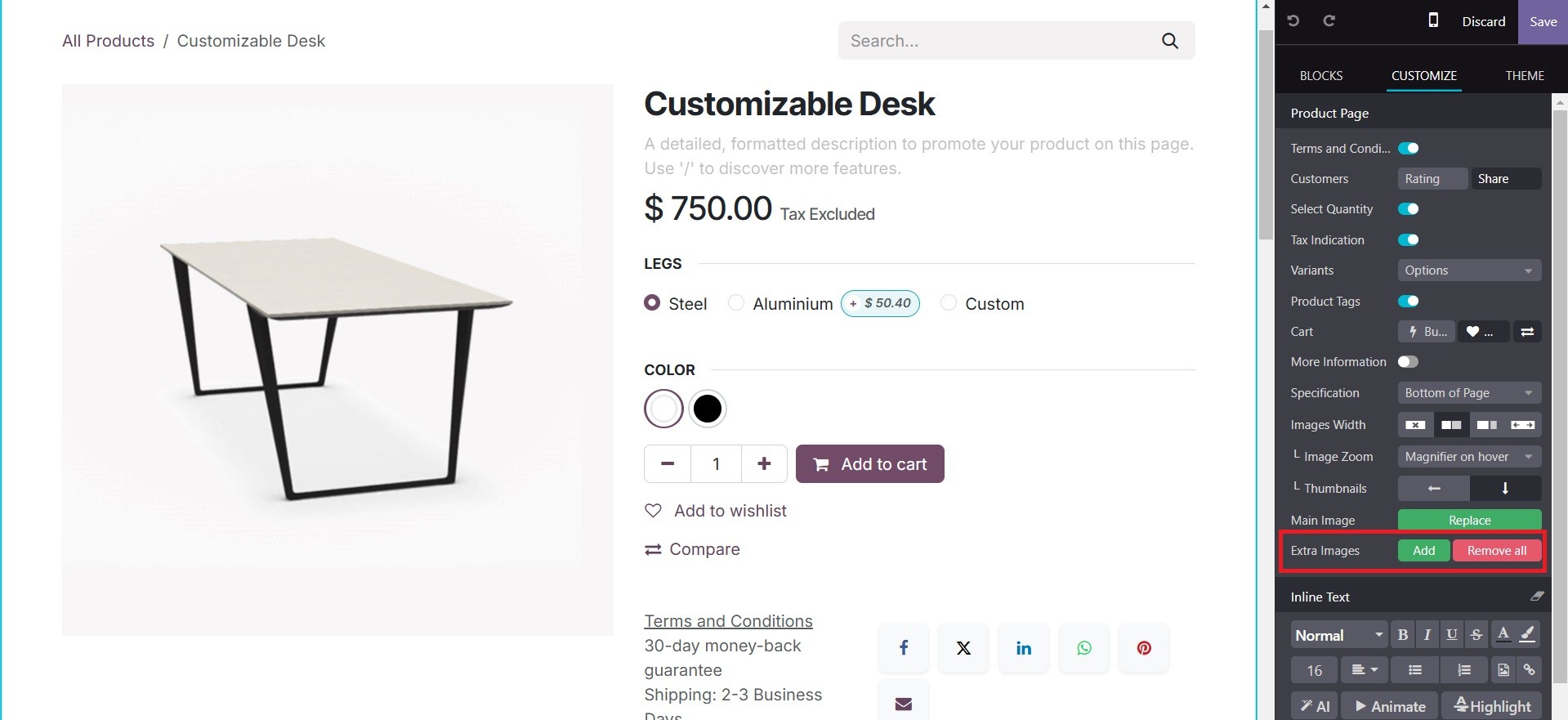
All of these photos are accessible to the buyer via the website, as shown below.
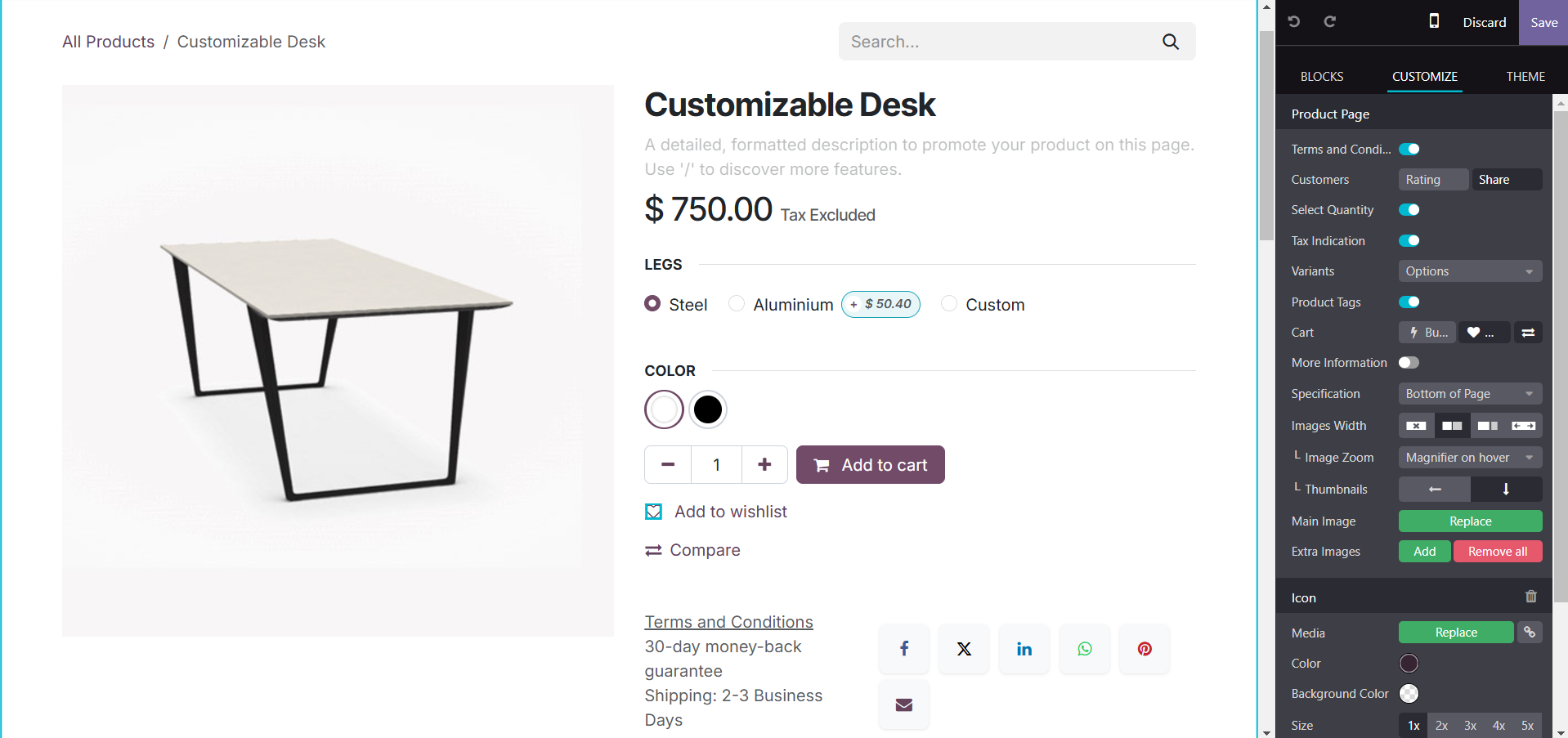
The image size will appear in the respective tab. The width field allows for formatting, picture width, and the conversion of the format to a web image, which will result in a compressed size. The quality of the image can be updated or altered. Similarly, the various parameters can be updated, like background image, visibility, animation, image formats, etc. Under the column section, you have the background, border, round corner, shadow, visibility, and animation.
Under the image section, you have the media and re-order option, which can be used to replace or remove the image accordingly.
accessible to the buyer via the website, as shown below.
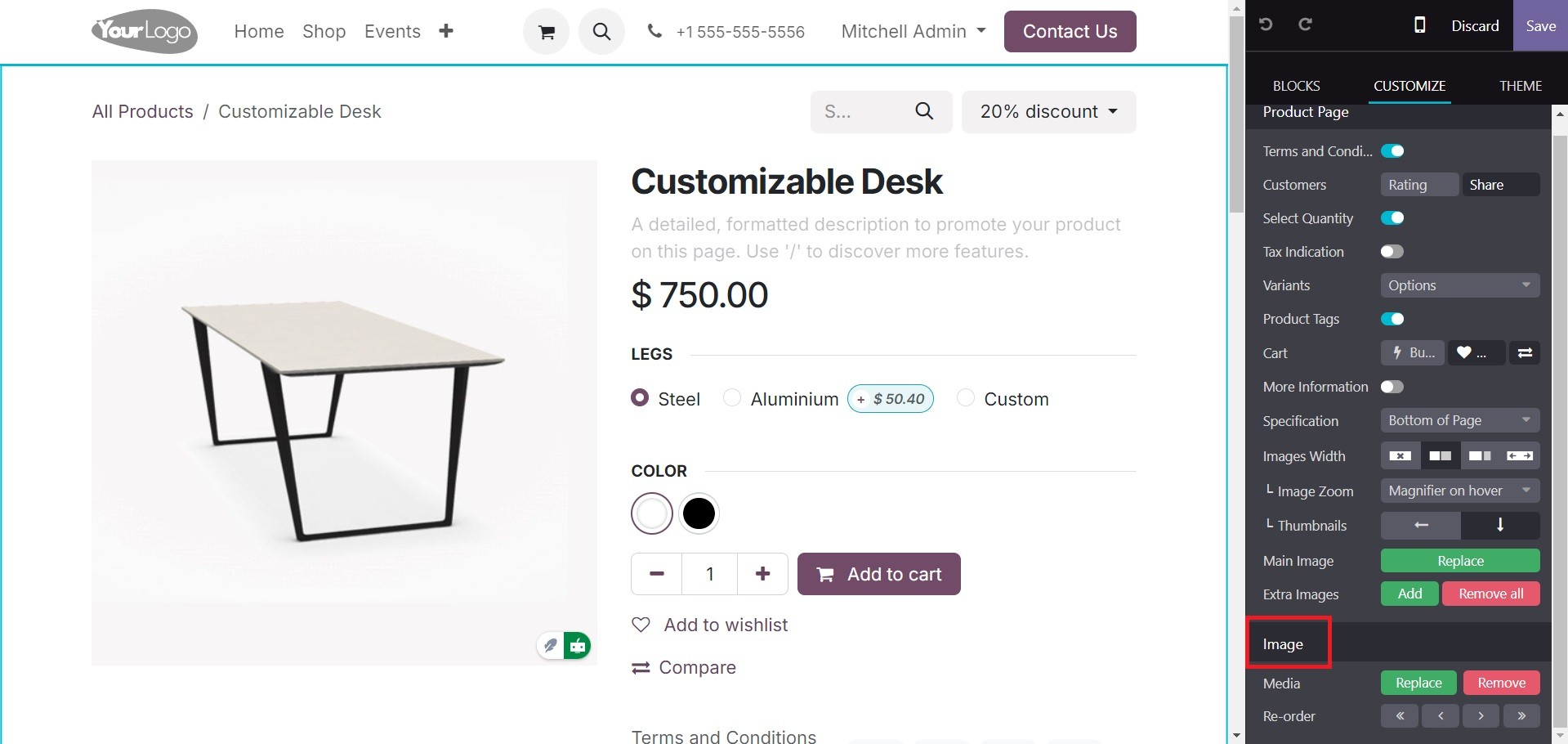
Customization is possible at different stages of the purchasing process
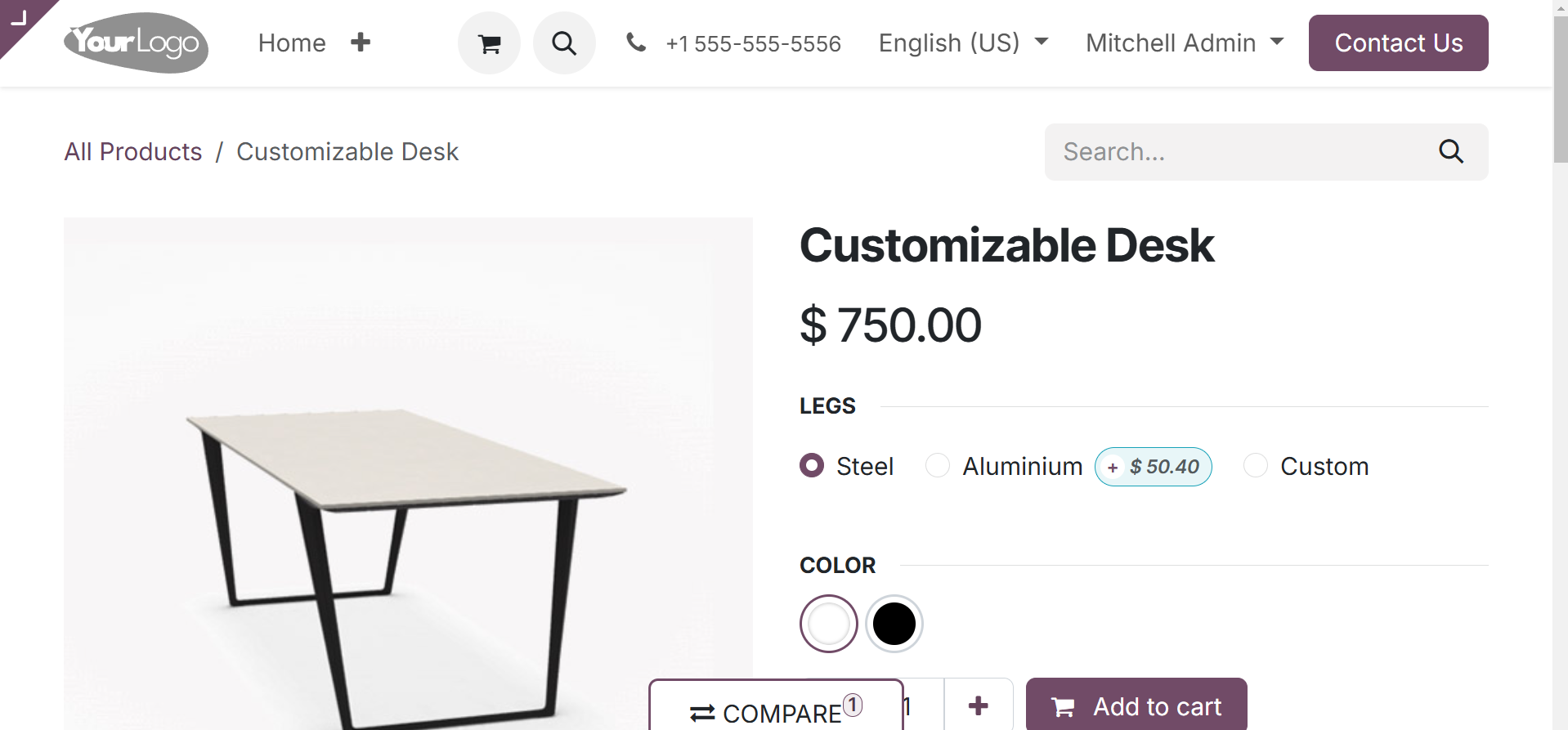
Users can quickly add a new product to the eCommerce website from the front end as well. To add a new product, click the New button, as in the image below.
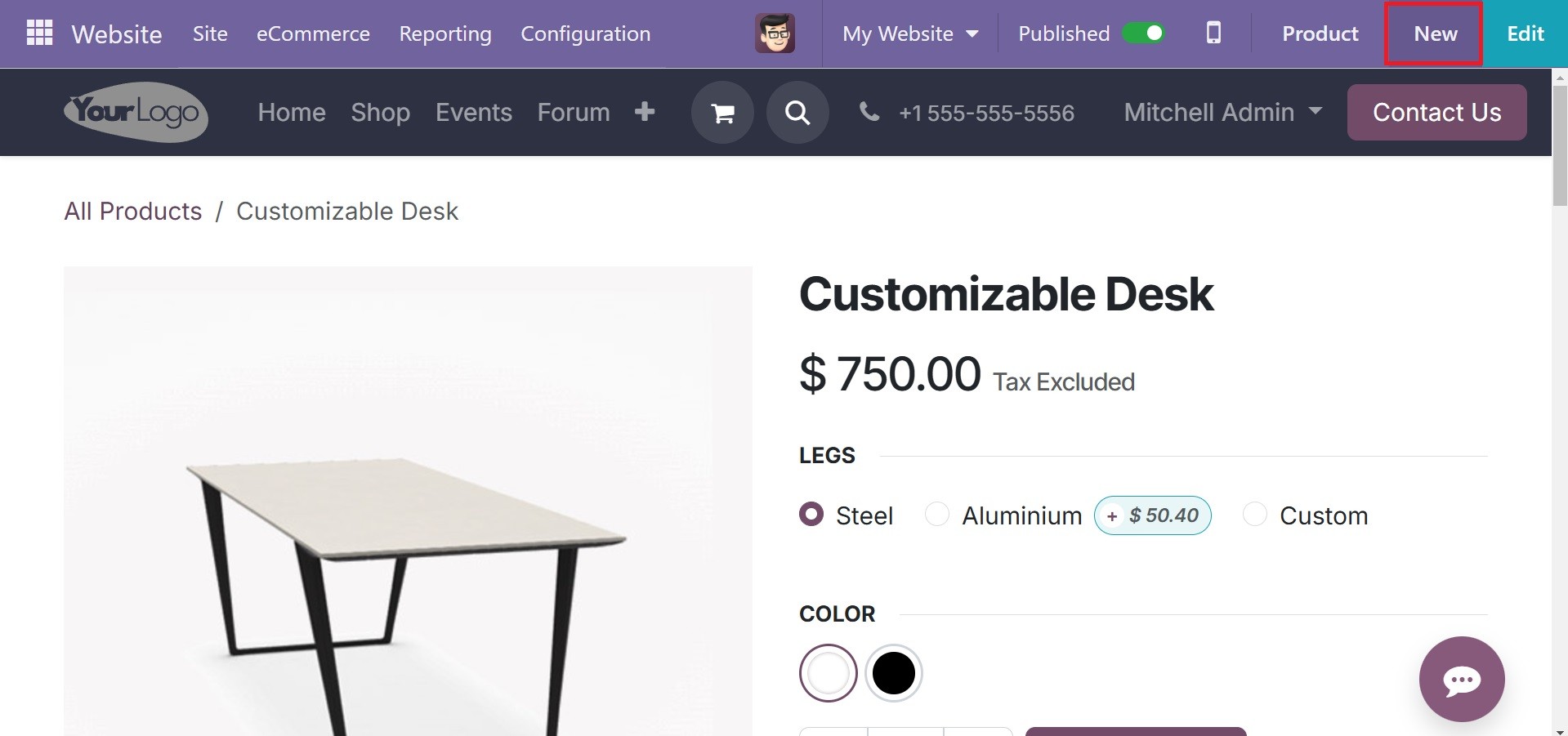
From the list of available options, which includes, among other things, pages, forums, and blogs, pick the Product option.
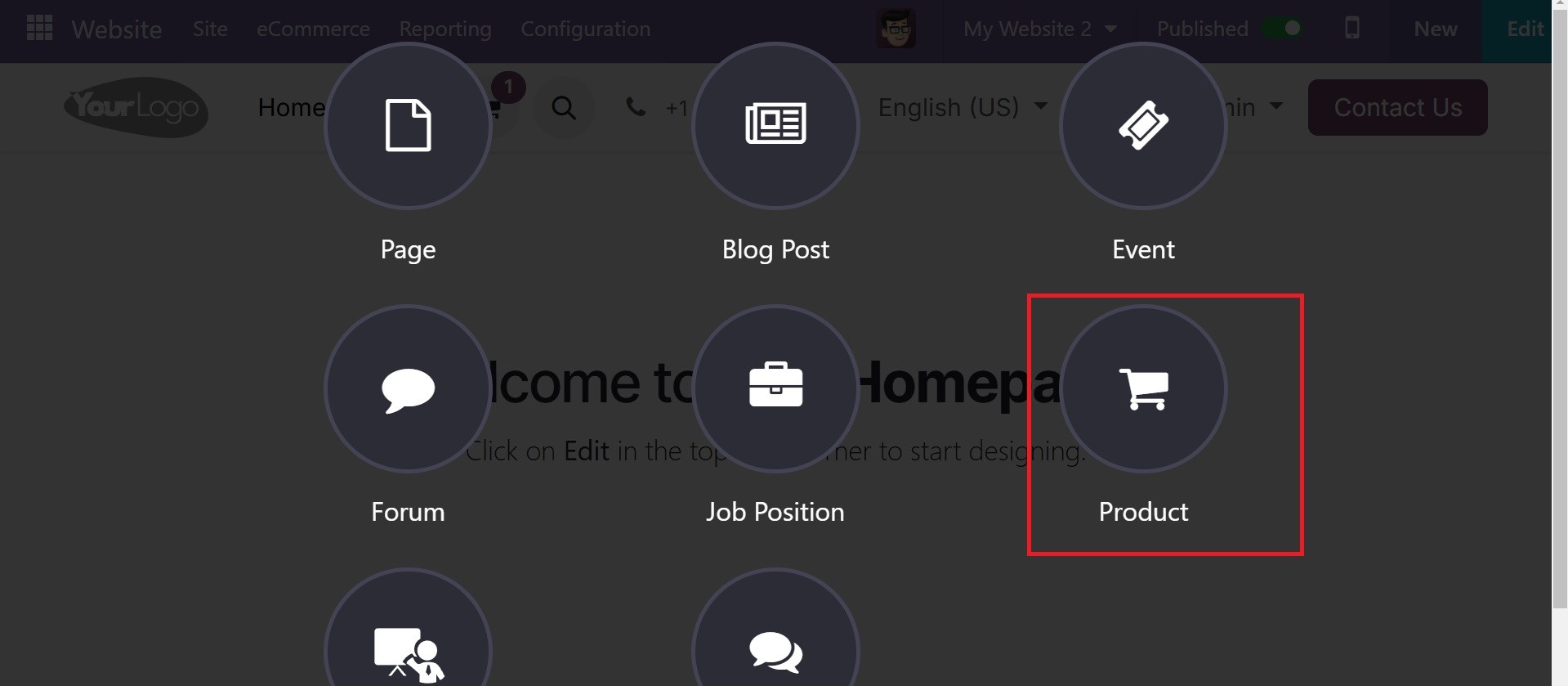
You can enter the product details in the new popup window that appears as a result. There, include the product name, customer tax, and sales price. After that, put the thing away.
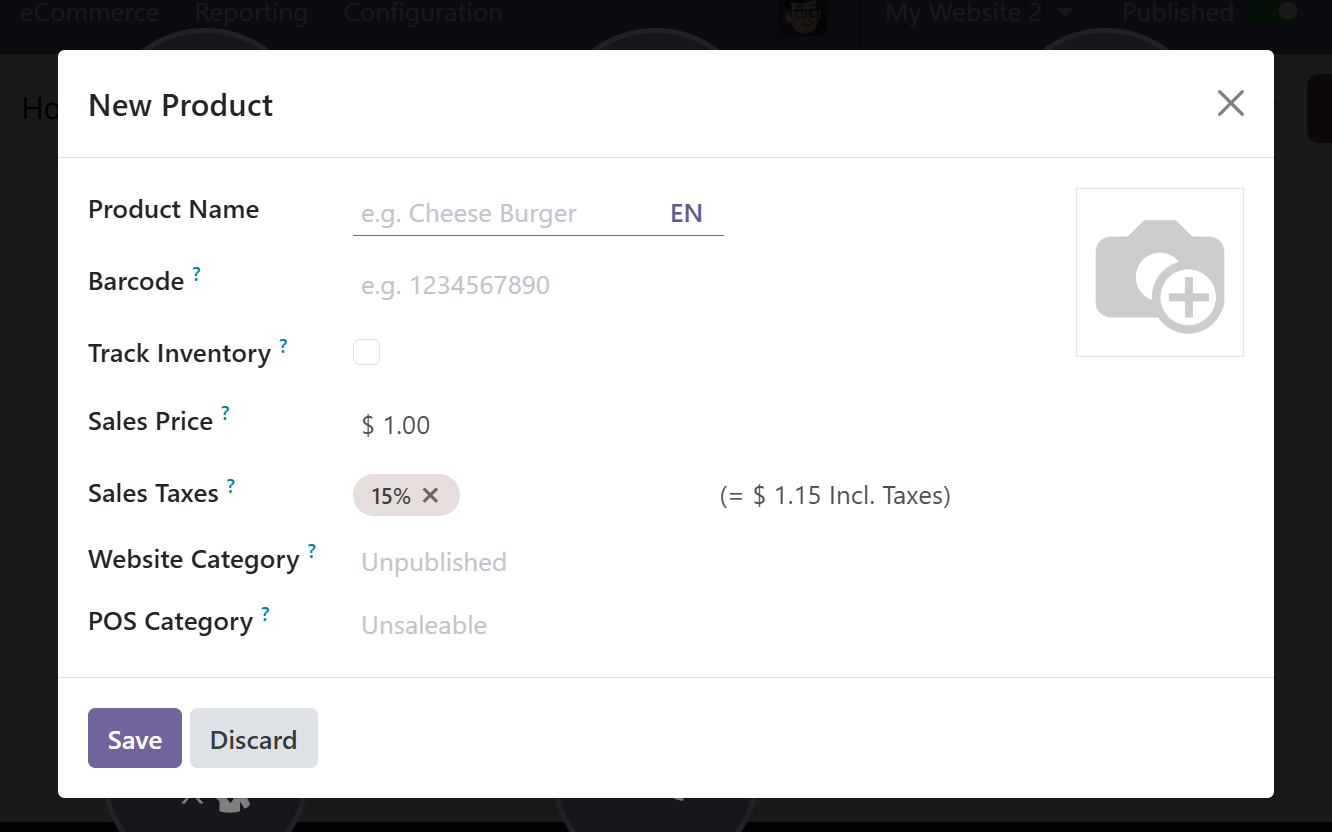
After that, users can alter this section to add more blocks and further personalize the website.
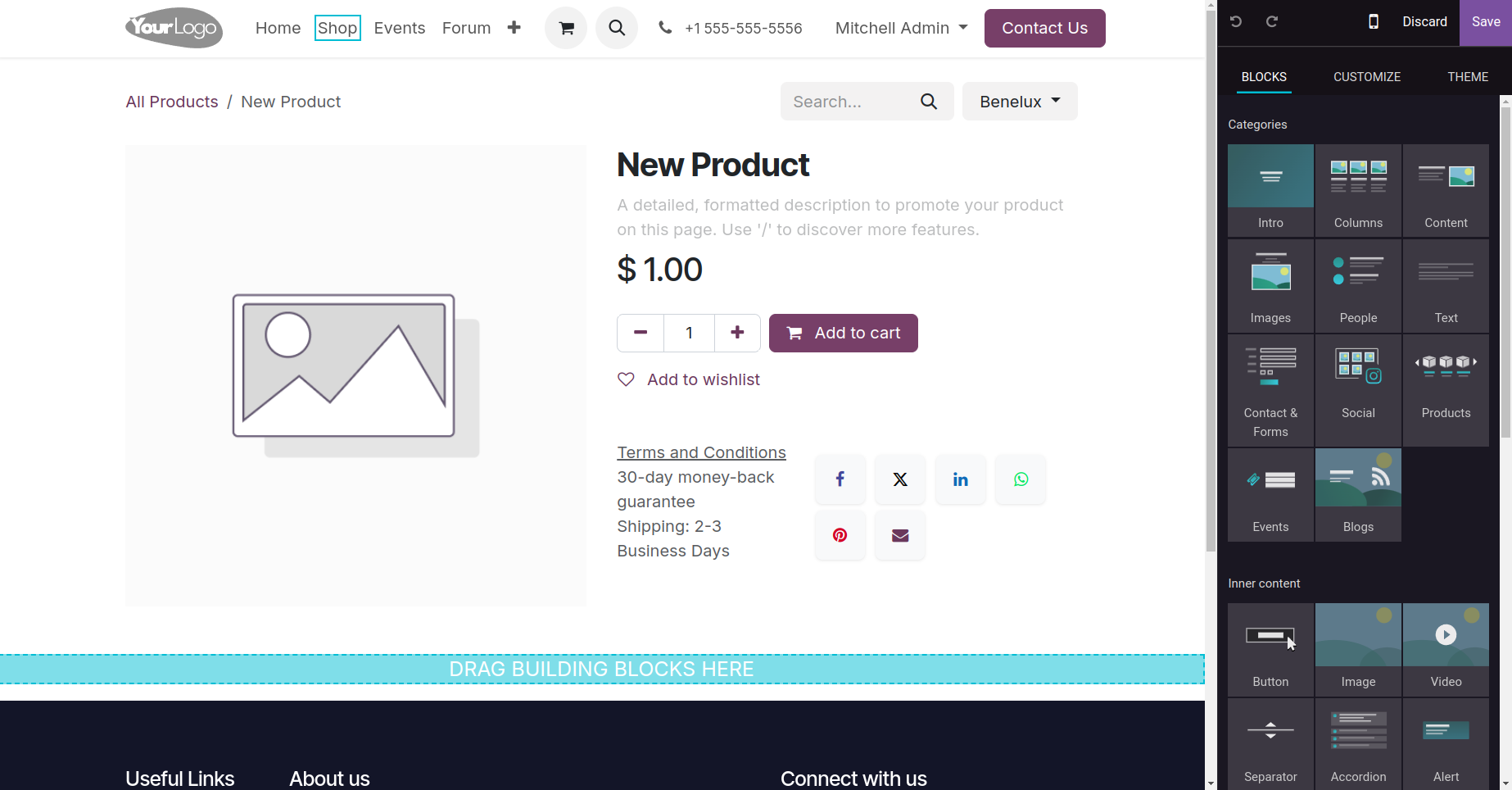
Users can add a picture of the product by selecting the Main Image option.
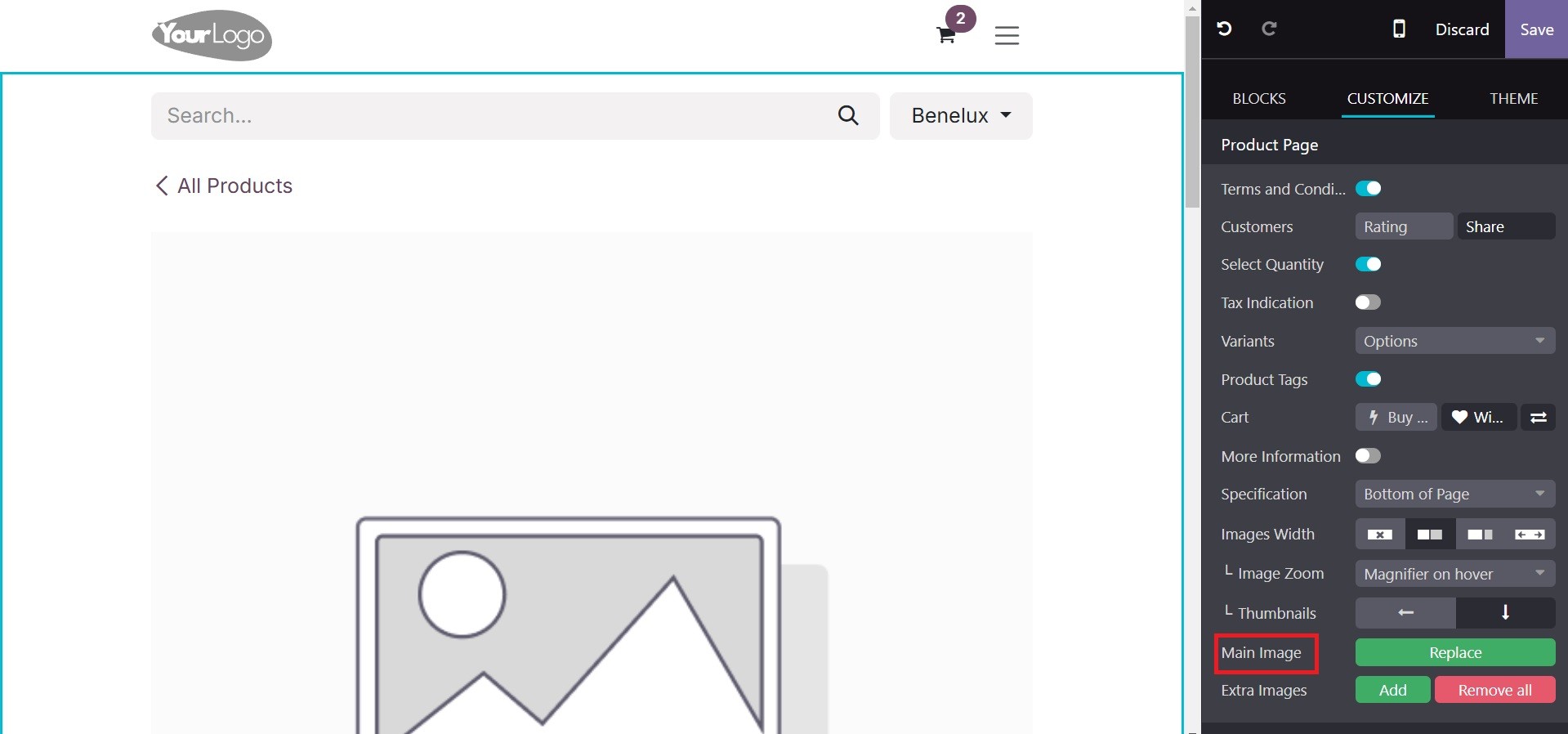
Within the CUSTOMIZE section, there is an Extra Images option. You can submit several photographs of the product on the website by using the Add button.
Other adjustments, including customer sharing and rating, can then be enabled. A new rating star can appear beneath the product name if the Customer Rating is enabled. Social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter are displayed next to the sharing terms and conditions in Customer Share choices.
Personalization also enables the view of comparison choices, buy, wishlist, and product variants. Details like the specifications, image width, layout, zoom, and thumbnails can then be supplied.
After you've completed all the required changes, click "Save." The product will thereafter be available on the website. Additionally, customization makes it possible to view product variations, buy options, wishlists, and comparison options. Then, you can provide information about the image width, layout, zoom, thumbnails, and specifications.
Advances in Technology and Ecommerce
From digital transformation and software-as-a-service to virtual reality and artificial intelligence, technology keeps pushing the limits of what ecommerce can do.
With compounding advancements in technology, there’s something new competing for online retailers’ attention every day. You’ll never find yourself at a loss for something new and different to try — the real task is identifying the best opportunities for your ecommerce business.
15 key AI use cases in ecommerce
How do you use AI in ecommerce? Research shows that AI can boost customer satisfaction, revenue, and cost savings by up to 25%, but knowing where to start can be challenging because the technology is evolving rapidly.
Here are the most impactful AI use cases in ecommerce:
1. Hyper-personalized product recommendations
Personalization is a key driver of customer engagement and loyalty, as a full 81% of shoppers favor brands that tailor their experience. AI-driven recommendation systems use machine learning (ML) and predictive analytics to track behavior, analyze preferences, and tailor shopping experiences to shoppers. Meanwhile, generative chatbots use NLP to recommend products to shoppers based on the business data they’ve been pre-trained on.
AI agents go a step further, tailoring the individual CX based on past and present data to deliver hyper-personalized recommendations. For example, a website shopping assistant agent can recommend products based on purchase history and preference, but also the current context of the conversation, user behavior, and even prior interactions stored in memory—providing a more accurate, relevant recommendation that increases the likelihood of conversion.
2. Proactively curb cart abandonment
Cart abandonment is the scourge of online retailers, but AI agents for ecommerce can help. Combining context awareness with goal-oriented behavior, AI agents can proactively trigger personalized offers at checkout to reduce cart abandonment.
For example, an AI agent can perceive when a shopper has stalled on the checkout page, then proactively trigger a coupon for free shipping or a discount in the split second before they bounce to help to close the sale.
3. Automated customer service with AI agents
Chatbots are a widely adopted form of AI in ecommerce, able to handle around 70% of customer interactions on their own. That said, AI agents are the next generation of shopping assistants, offering a more seamless support experience without the usual friction.
Like chatbots, AI agents use NLP to understand and respond to customer inquiries in a conversational way with accurate, relevant responses. Available 24/7 on websites and support channels, agents can provide immediate support, answer FAQs about shipping and returns, recommend products, even execute tasks like transaction processing.
Unlike chatbots, AI agents can remember past interactions with customers. This enables them to hold a single continuous conversation with customers that spans channels, eliminating the friction of playing catch-up with returning customers. By maintaining context between interactions, AI agents enable a more convenient, efficient service experience that elevates customer satisfaction and loyalty— while freeing human agents for more complex tasks.
4. Dynamic pricing optimization
AI helps retailers to maximize profits by optimizing prices to current market conditions. Using ML algorithms, AI-driven pricing tools analyze internal and external factors like product availability, demand history, production cost, and average online price to dynamically set prices for optimal profitability.
For example, Amazon uses AI-powered dynamic pricing tools to optimize prices as often as every 10 minutes, helping the retail giant to increase profits by 143% annually on average. In effect, if demand for a certain product spikes, AI bumps up the listed price automatically. Or when a competitor slashes prices, AI drops the price on your site to match.
With an AI-driven pricing optimization strategy, retailers can improve inventory management, optimize personalization, and maximize revenue in the face of ever-changing market conditions.
5. Conversational commerce with AI voice-assisted shopping
Voice-assisted shopping and search are gaining traction among shoppers, with 22% of people saying they prefer voice-enabled AI assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant to typing. By integrating NLP and voice recognition technology into websites and support channels, retailers can offer a more convenient experience that drives sales among the millions of consumers who already use voice-enabled AI to shop and discover new products.
AI agents are perfect for voice-assisted shopping and search. They can guide customers through the shopping process from start to finish with a live conversation, seamlessly shifting from comparing prices to processing transactions to handling returns or exchanges. And since AI agents for ecommerce are omnichannel, if the customer switches channels, all previous shopping activity is preserved—helping to increase sales, operational efficiency, and CX in ways gen AI chatbots can’t.

Become a Certified E-Commerce Marketing Master
Discover how to create compelling content for users and search engines alike. Gain expertise in diverse digital marketing topics like SEO, social media, email, and more!
6. Smarter search capabilities
AI enhances the search capabilities of websites and mobile apps, making it faster and easier for shoppers to find the products they want. Retailers can integrate the following AI technologies to supercharge their product discovery process:
- Natural language processing (NLP): Enables site search engines to understand the meaning and intent behind a user’s search query in any language to deliver the most relevant results—even if the search query contains variations like typos, synonyms, or slang.
- AI-assisted visual search: Enable customers to search for products by uploading an image instead of typing. Employs AI algorithms and image recognition tech to suggest items similar to what’s pictured, improving discovery among customers that don’t know the product name.
- Context-based search: Uses AI algorithms to scan external data like trending products, seasonality, and day of the week to make more relevant search results. Can also auto-fill search phrases and suggest related products to increase the likelihood of a purchase.
7. Improved customer segmentation and marketing
Audience segmentation is essential to effective personalized marketing, and AI in ecommerce can help. Using ML, AI-driven tools for customer segmentation analyze user data and identify patterns across datasets, then create accurate customer segments based on shared characteristics—even discovering entirely new segments and characteristics that may have been overlooked.
This enables retailers to tailor marketing strategies and target campaigns with surgical precision, ultimately reaching, engaging, and converting audiences more effectively. In fact, well-segmented marketing campaigns have been shown to drive a potential 760% increase in revenue.
8. Intuitive upselling and cross-selling
AI can anticipate which products will appeal to customers and recommend these items in opportune moments to drive upsells and cross-sells. Combining ML algorithms with predictive analytics, AI-driven recommendation systems analyze past purchases, preferences, and browsing behavior to tailor experiences across websites, chatbots/shopping assistants, and mobile apps to the tastes of individual customers.
Dynamic website content is an example of this AI use case in ecommerce, such as the “You might also like” sections on websites or the “Frequently bought together” product bundles on checkout pages. In fact, 63% of consumers say AI-powered product recommendations are highly influential on their purchases.
9. Auto-generated content
With generative AI for ecommerce, retailers can automatically create highly tailored content that drives greater engagement and sales—but at a fraction of the time and cost. Based on the customer profile and current behavior, gen AI tools can create a variety of content tailored to specific experiences and audience segments, such as:
- Product descriptions
- Marketing content
- Dynamic website content
- Personalized product recommendations
10. Fraud detection and prevention
Protecting retailers against fraudsters in real-time is another key AI use case in ecommerce. AI-powered fraud detection tools use advanced ML algorithms to analyze transactions, behavioral data, IP addresses, credit card information, and more to detect complex patterns and irregularities that suggest fraudulent activity.
Going a step further, AI agents can take action to halt fraudulent transactions in the moment. For example, a vertical AI agent for fraud prevention on a website can require additional verification from suspicious buyers before authorizing a purchase, while flagging the high-risk transaction for the fraud team.
11. Fake review detection
Customer reviews are key to building trust and driving sales, as 93% of online shoppers read reviews before making a purchase. However, research shows that around 30% of online reviews are fake, which can seriously erode trust and conversions if left up.
Using NLP and machine learning, AI can quickly analyze text patterns, writing styles, and formatting to identify and flag suspicious reviews. Amazon, for example, uses advanced language models and big data analytics to evaluate seller reviews, considering data points like previous reports of abuse, review histories, and even ad investments (which can incentivize fake reviews).
12. Supply chain optimization
Beyond enhancing CX, AI enables retailers to increase operational efficiency and reduce costs by automating repetitive tasks and decision-making processes in the supply chain. Some of these key AI in ecommerce use cases include:
- Smart logistics systems: Use AI agents in Internet of Things (IoT) devices like sensors, radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags, and smart shelves to monitor real-time inventory levels—reducing manual effort, driving efficiency, predicting demand, and optimizing production costs.
- Route optimization: AI optimization algorithms consider factors like transportation networks, traffic, and weather in real-time to determine the most efficient delivery routes and reduce transportation costs. Alibaba, for example, reduced costly delivery errors by 40% using AI.
- Order tracking: AI enables continuous real-time order tracking, providing visibility into the location and status of inventory shipments and customer orders along the last mile, helping to improve both customer satisfaction and warehouse operations.
13. Sales and demand forecasting
AI significantly improves the accuracy of demand forecasting as a part of supply chain optimization. By analyzing sales data, demographics, customer behavior, plus external factors like weather and customer reviews, AI algorithms can predict demand with surgical precision then adjust inventory levels accordingly to maximize profitability.
By factoring in lead times plus variable demand from seasonality and on-off events, AI minimizes the risk of stock outs while preventing overstocking. AI agents enhance these capabilities with real-time data on market conditions, breaking news, shopper behavior, and more—allowing retailers to remain agile in evolving marketing conditions while always having what customers want.
14. Streamlined inventory management
Similarly, AI can streamline inventory management by turning real-time data into more efficient, profitable operations. By analyzing data on sales patterns, lead times, and market trends, AI algorithms can calculate the optimal stock levels for each product, ensuring the optimal inventory levels while minimizing carrying costs.
Robots with AI image recognition technology can also assist with real-time inventory and warehouse management. Using data-capture cameras, these AI-equipped robots cruise up and down warehouse aisles, storing, retrieving, and tracking stocked items to automate inventory management without adding to headcount.
15. Omnichannel customer engagement at scale
AI agents are interoperable across systems, meaning they function as the bridge between otherwise disjointed ecommerce platforms and channels—even unstructured data environments like email and social media. Effectively, this makes the dream of a truly seamless omnichannel customer experience an operational reality for online retailers.
By integrating AI agents across the shopping journey, businesses can automate customer engagement and customer service at scale. AI agents integrate seamlessly with any component in their environment, moving real-time data between tools and systems to create a single unified AI-powered system.
By serving as the go-between for disparate ecommece technologies, AI agents are poised to bring new levels of automation, personalization, and actionable business intelligence to retailers, delivering a 360 degree customer view that informs better decisions and automated engagement at scale.
Driving & Enhance E-Commerce Forward with Odoo 17 AI-Powered
Driving & Enhance E-Commerce Forward with Odoo 17 AI-Powered course is the ultimate resource for professionals who want to understand and utilize AI’s transformative potential. It is the blueprint for understanding and applying AI, giving your business just the edge you’ve been waiting for.