What is accounting in business, and why is it important?
Accounting can seem like a daunting, catch-all term, but at its core, it’s simply the systematic recording, reporting, and analysis of your business’s financial transactions. Even if you aren’t legally obliged to present your financial statements, accounting is a critical part of tracking your profitability, controlling your cash flow, and making informed decisions.
For small businesses, the key components of your accounting responsibilities should include:
- Bookkeeping: Tracking daily transactions and maintaining organized financial records.
- Financial reporting: Creating reports that summarize your business’s financial health, such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Tax compliance: Meeting tax requirements by accurately documenting income, expenses, and payroll data, and filing and reporting correctly.
Without organized accounting practices in place, your business can easily fall behind on taxes, miss opportunities to cut costs, or overlook growth potential.
What are the basic accounting fundamentals?
To set up an effective accounting system, it’s essential to grasp the core elements involved. These form the foundation of accounting and are vital for keeping track of your company’s financial health.
These concepts are tracked in the following standard financial statements:
Income statement
An income statement — also known as a profit and loss (P&L) statement — shows your company's revenues, expenses, and profits or losses over a specific period (usually a quarter or a year). It provides a snapshot of how well your company is performing financially by detailing its revenue generation and operational costs.
The main elements of an income statement include:
- Revenue: The income you generate from selling your products or services.
- Cost of goods sold (COGS): The direct costs related to producing the goods or services sold by your company.
- Gross profit: The total you get when subtracting COGS from revenue.
- Operating expenses: The costs associated with running the business, such as salaries, rent, and utilities.
- Operating income: Your gross profit minus operating expenses.
- Other income and expenses: Non-operating items like interest income, gains or losses from investments, and taxes.
- Net income: The bottom line, showing your total profit or loss after all revenues and expenses have been accounted for.
The income statement is essential for understanding profitability and is also used by stakeholders, such as potential investors and creditors, to assess your company’s financial health and performance over time.
Balance sheet
A balance sheet provides a snapshot of your company's financial position at a specific point in time. It details what your company owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and the value remaining for shareholders (equity). The balance sheet is based on the fundamental accounting equation:
Assets = liabilities + equity
The main components of a balance sheet are:
Assets
These are the resources owned by your company and are typically divided into:
- Current assets: Assets that are expected to be converted into cash or used up within one year, such as cash, accounts receivable, and inventory.
- Non-current assets: Long-term investments, property, plant, equipment, and intangible assets (like patents) that provide value over a longer period.
Liabilities
These are your company's obligations and debts, split into:
- Current liabilities: Debts or obligations that your company must pay within one year, such as accounts payable and short-term loans.
- Non-current liabilities: Long-term obligations like bonds, loans, or deferred tax liabilities.
Equity
Equity refers to the owner’s (or shareholders') interest in the business after liabilities are subtracted from assets. For startups and small businesses, this usually includes:
- Owner's equity (or shareholder’s equity): The initial investment made by the owner(s) or shareholders.
- Retained earnings: The profits kept in the business to fund growth rather than be distributed as dividends.
Cash flow statement
A cash flow statement tracks the inflows and outflows of cash in your business over a specific period. It helps you understand how cash is generated and spent, showing whether your company has enough liquidity to cover expenses, invest in growth, and handle unexpected costs. This statement is essential for managing cash, especially for small businesses and startups, where cash flow is often tight.
Accounting and Business Administration-Advanced Certificate
designed to provide the learners with the required knowledge and hands-on skills needed to compete in the job market.
The cash flow statement is divided into three main sections:
Operating activities
This section shows cash flow related to the core operations of your business, such as:
- Cash inflows: Revenue from sales, collections from accounts receivable, and other operating income.
- Cash outflows: Payments for expenses like rent, salaries, utilities, taxes, and payments to suppliers.
A positive cash flow from operating activities usually indicates that your business is generating sufficient cash from its core activities to sustain operations.
Investing activities
This section shows cash used for long-term investments and purchases, such as:
- Cash inflows: Proceeds from selling assets, equipment, or investments.
- Cash outflows: Cash spent on purchasing assets like equipment, property, or other businesses.
For startups, this section often reflects cash spent on growth initiatives, like acquiring new equipment or investing in product development.
Financing activities
This section details cash flow related to funding the business, such as:
- Cash inflows: Money raised through loans, credit lines, or investments from owners or investors.
- Cash outflows: Payments made to repay loans, pay dividends, or buy back shares.
For startups, financing activities may primarily reflect funds raised from investors or loans taken to support early growth.
A cash flow statement provides a clearer picture of liquidity by showing actual cash movement rather than just profit or loss. This helps you to more effectively monitor your cash reserves, make informed spending decisions, and prepare for potential cash shortages. It’s particularly useful for identifying trends in cash flow that could affect your company's ability to grow or sustain its operations.
Business accounting software explained
Accounting software refers to computer programs or applications designed to facilitate and streamline financial management and recordkeeping tasks within a business or organization. It serves as a digital tool to record, organize, and analyze financial data, enabling businesses to effectively manage their finances, track transactions, generate reports, and ensure compliance with accounting principles and regulations.
Accounting software typically provides features and functionalities such as:
- General ledger management
- Accounts payable and receivable tracking
- Inventory management
- Payroll processing
- Financial statement generation
- Budgeting
- Tax management
These software solutions automate various financial tasks, reducing manual errors, improving efficiency, and saving time for businesses.
With accounting software, companies can maintain accurate and up-to-date financial records, track income and expenses, manage cash flow, generate invoices and financial records, reconcile bank statements, and make informed financial decisions. Accounting software offers a centralized platform for financial information, allowing businesses to monitor their financial health, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to drive growth and profitability.
Overall, accounting software plays a crucial role in simplifying and streamlining financial processes, enhancing accuracy, and providing valuable insights into an organization’s financial performance.
Ten key features business accounting software should have
Every accounting software must effectively manage essential accounting tasks, like recording transactions, tracking payments, and generating financial statements. However, as companies expand, they often require additional functionalities. Thus, it is vital to carefully evaluate capabilities when selecting accounting software, ensuring it can meet both current and future requirements and that it has these key features:
General ledger management
The general ledger is the central repository for all financial transactions within a business. Look for accounting software that offers robust general ledger capabilities, which allows the tracking and management of financial data.
The accounting software an organization chooses should offer comprehensive support for fundamental accounting tasks, including transaction recording and categorization, general ledger and charts of accounts (COA) management, and the generation of financial statements and reports.
Accounting software should automate basic bookkeeping and workflows, such as creating journal entries, reconciling accounts, and performing basic. Some software enables users to toggle quickly between the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) standard used in the United States and the international financial reporting standards (IFRS) used in other countries. This feature is especially beneficial for growing businesses with international operations.Accounts payable and receivable
Efficiently managing accounts payable and accounts receivable processes is crucial for maintaining healthy cash flow. Look for software that provides tools for tracking and managing invoices, payments, and outstanding invoices.
Accounting software offers the advantage of expediting cash flow by automating invoicing and collection processes. It enables efficient management of accounts receivable by automatically generating invoices, overseeing credit terms, and improving payment collection through automated alerts and multiple payment methods. The software empowers accounts receivable staff to monitor the status of outstanding invoices, access customer payment history, and track key performance metrics like days sales outstanding (DSO).Financial reporting with business accounting software
Generating accurate and comprehensive financial reports is essential for monitoring the financial health of a business. Choose software that offers a variety of financial reporting options, including balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements, and customizable reports.Bank reconciliation
Bank reconciliation is the process of matching a business’s financial records with its bank statements to ensure accuracy. Accounting software with built-in bank reconciliation features can simplify and streamline this process, saving time and reducing errors.Budgeting and forecasting
Creating budgets and forecasts allows organizations to plan and track financial performance. Look for software that includes budgeting and forecasting tools, enabling users to set financial goals, monitor progress, and make informed decisions.
By utilizing both historical and real-time data, businesses can generate budgets and forecasts that aid managers in predicting future business performance. These budgets serve as a benchmark against which actual performance can be tracked, enabling the identification and resolution of any issues. Managers and financial experts can delve into the specifics to identify areas where the budget has been exceeded, promptly address concerns, and make necessary adjustments to enhance business performance. Analyzing this information also enriches the ability of a business to generate more precise forecasts for future periods.Tax management
Accounting software with tax management features can help companies stay compliant with tax regulations and simplify the tax filing process. Be on the search for software that supports automated tax calculations, provides tax forms, and generates reports to assist with tax preparation.Inventory management
If a business deals with physical products, having inventory management capabilities within accounting software is essential. Check for features that allow the tracking of inventory levels, management of stock movements, and generation of inventory reports.Payroll processing
Payroll management can be complex and time consuming. Accounting software that includes payroll processing features can automate tasks such as calculating wages, generating pay slips, and filing payroll taxes, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
As businesses expand, manual calculation and management of payroll becomes increasingly complex. Factors adding even more difficulty to ensuring workers get paid on time and at the proper amount include:- Multiple pay scales
- Overtime
- Benefits
- Sales commissions
- Contract workers
Integrated payroll management software automates various payroll calculations, including gross and net pay, payroll tax withholdings, and health and retirement benefits. It also generates necessary forms such as W-2s and 1099-MISCs, among others. This software ensures accurate collections and filings of local payroll taxes in different jurisdictions, making it an essential feature for businesses operating in multiple states or countries.Multi-currency support in business accounting software
For businesses operating internationally or dealing with multiple currencies, accounting software with multi-currency support is vital. This feature enables organizations to process transactions, record financials, and generate reports in different currencies.Integration and scalability
Organizations should consider whether the accounting software can integrate with other business systems they use, such as customer relationship management (CRM) or inventory management software. Additionally, be sure the solution of choice can accommodate expected growth and handle increased data volumes as a business expands.
Get Started with Accounting Basics
The process of reporting, documenting, illustrating, and summarizing financial data is referred to as accounting. An organization or business cannot function without accounting. It serves as the primary point of contact for all types of commercial dealings. Accounting has been refreshed over the years as a contained system for maintaining financial records and supporting an accountant's responsibilities. However, the continually changing business climate in the present day necessitates that business owners and accountants reevaluate their roles and duties. Accounting involves more than just creating financial reports and keeping track of books.
Significance of Accounting
Accounting, which is the systematic and thorough recording of a company's financial activities, is essential to its operation, including managing statutory compliance and tracking income-expenditure relationships. Additionally, gathering quantitative financial data is beneficial. The owners, management, investors, and even governments will gain from the accounting system. A company that succeeds needs a solid and well-established accounting and bookkeeping system.
The bookkeeping procedure serves as the foundation of the accounting system, which monitors a company's financial health. At the end of each fiscal year, statistics and information are reported in the form of a financial statement.
Accounting is essential for assessing business performance effectively. Comparing accounts with prior years is simple. By maintaining a strong book of accounts, the accounting system also enables you to keep a careful eye on the cash flow. The account-keeping system also makes filing simple and ensures that you never break the law.
In addition to all of these advantages, accounting data makes it simple to create a budget that will support a given business strategy. So that you can budget for your future ambitions in an efficient and productive manner. An organization can benefit from proper accounting by receiving the numerous financial reports needed to manage day-to-day operations.
The management of the budget, one of the most crucial components of an organization, will be incredibly easy if the accounting system is reliable. Making the proper company decisions will be aided by the accurate data you obtain from the financial accounts, which will lead to efficient administration and increased profitability.
Accounting and Business Administration-Advanced Certificate
designed to provide the learners with the required knowledge and hands-on skills needed to compete in the job market.
Account Groups
Account Groups are formed by grouping together related ledger accounts. The hierarchy of ledger accounts is supposed to be demonstrated by these account groups. The generation of relevant reports will greatly benefit from this structure of ledger accounts. Regular, Payable, Receivable, and Liquidity account groups are the most frequently utilized account types in Odoo17.
1. Account Receivable ( Debtors )
The sum of money necessary for paying for goods or services that have been received but have not yet been paid by the customer is known as an Account Receivable. The debtors are another name for the Account Receivable. These accounts are particularly practical for keeping track of all customer receivables. The receivables will fall under the Assets when we take their nature into account. When taking into account a sale, the receivable accounts are debited based on the increasing amount of receivables.
2. Bank and Cash
Every organization's bank and cash account will fall under the Bank and Cash type because it is an Asset by definition. As an illustration, let's say a company decides to make a cash payment rather than a credit purchase and takes into account the amount that is taken out of the bank account. Due to the asset's decrease, the bank account will be credited.
3. Current Assets
Cash and other assets that are planned to be converted to cash within a year are considered Current Assets. So, registering short-term assets will be facilitated by using this account type. This category can include assets like inventory, short-term investments, prepaid expenses, etc. This category includes the bank deposits, loans, and advances provided to the employees.
General accounts include Stock Valuation Accounts, Stock Input and Output Accounts, Deferred Expense Accounts, and numerous others. Because they are assets by nature, Odoo's "Current Assets" ledgers and entries of this sort have an impact on the balance sheet.
4. Non-Current Assets
Non-current assets are regarded as assets that the company purchases or invests in. That investment's quantity does not, however, reverse within an accounting year. As a result, this investment type will produce returns for a considerable amount of time and cannot simply be converted into cash. The following are some examples of this kind of asset: properties, automobiles, insurance, etc. It is impossible to determine the total value within the accounting year. The balance sheet includes a list of each one of them.
5. Prepayments
Prepaid expenses serve as an example of prepayments. Although the goods and services in this instance have already been paid for, they have not yet been received or used. As an illustration, Odoo saw prepaid or deferred expenses as belonging to this category.
For instance, suppose there was insurance with a $30,000 annual payment. The company won't be able to include the entire expense in the current-year profit and loss report. The sum must be spread out over a full year by the organization. As a result, $2500 will be used each month, and the expense will be recorded. The payment will be of the type "Asset," and the asset value will drop annually. Therefore, as the expense steadily reduces, the payment account will be credited and the expense account debited.
6. Fixed Assets
The Fixed Assets account type is highly convenient for recording all fixed asset transactions, including those involving equipment, vehicles, real estate, buildings, furniture, and many more. All the goods that the firm or business intends to use for a long time can be included. Additionally, fixed assets fall under the Assets category. As a result, when we make a purchase, the fixed asset will grow, the fixed asset account will be debited, and the fixed assets will be recorded on the balance sheet.
7. Payables
Creditors is another name for the Payables account category. It is the total amount owed by an organization to anyone or any individual. The payables accounts are appropriate for keeping track of all amounts owed to vendors or suppliers. The payable account is additionally credited as the category of responsibility on a vendor bill.
8. Credit Cards
Another category of account is the credit card, and this account's characteristic is liability. The balance sheet includes information about the credit card. In the case of credit cards, the amount of money spent using the card for any purpose, such as making a purchase or paying for other expenses, will result in certain debts, which we need to repay within a certain amount of time, usually less than or close to two months.
9. Current Liabilities
Short-term liabilities are Current Liabilities, those that must be paid off within a year. The Current Liability Account Type can be listed under the following headings. Among them are overdrafts at the bank, quick loans, taxes and duties, salaries that must be paid, payroll taxes, accruing costs, income taxes, and many other things.
10. Non-current liabilities
Non-current liabilities, also known as long-period debts or financial commitments, are long-term obligations that are shown on the balance sheet and are due in a year or more. Non-current liabilities include things like pension benefit obligations, long-term loans, deferred tax liabilities, and long-term leasing obligations.
11. Income & Other Income
When a company wants to show its income or revenue, the Income & Other Income account type is quite helpful. The nature of the account is income, which will be included in the profit and loss reports. The company's primary source of income is from the sale of its goods and services. And any other income is not considered to be a direct source of revenue. Interest payments, rent payments, and other sources of revenue are a few examples.
12. Expenses
The account types known as expense accounts are used to keep track of every aspect of how much an organization spends on regular expenses over the course of a certain accounting period. This form of expense account comprises delivery costs, income tax costs, costs associated with the creation of goods and services, salary costs, advertising costs, maintenance costs, marketing costs, rent costs, etc. Since expenses are the nature of the Expense accounts type, they will be included in the income statement/profit and loss report.
13. Depreciation
The amount that an organization's assets are depreciated for a particular period is generally referred to as the Depreciation account type. This account type is typically used to track the depreciation of fixed assets. There will occasionally be some depreciation in the case of fixed assets, and each period will undoubtedly see a decline in their value. Depreciation of this kind will, therefore, be linear or regressive. At the time an asset is created, it will also have a book value and a salvage value. The initial cost is represented by the book value. Salvage value is the amount that an organization will receive when selling a fixed asset after all depreciation has been accounted for. Furthermore, based on the depreciation method used, the expense will be spread out over a specific time period as opposed to being added all at once to the current year. The expense account is credited, while the depreciation accounts debit.
14. Cost Of Revenue
The direct costs associated with the company's goods and services are closely correlated with the cost of revenue. This means that it represents the full cost of producing and providing a good or service to customers. It is more comfortable to depict the direct cost linked with the goods and services since it is immediately related to the income statement. It comprises the price of producing the goods and shipping it to the buyers. Cost of revenue is an expense by definition, and as such, this account type will have an effect on gross profit.
15. Equity
The equity account type can be thought of as the financial representation of a company's intellectual property. It displays the sum of money that the employers contributed to beginning operations. Equity can result from a business receiving payments from its owners or from the residual income it generates. In other words, equity is the amount of assets remaining after all liabilities have been paid in full and are recorded on the balance sheet. This account type includes common stock, contributed surplus, treasury stock, common and preference stocks, other sizable earnings, etc. Equity will fall under the category of Asset type when we think about its nature. The equity will be equal to the amount of money invested. Therefore, any investment will result in an increase in equity. The extra equity will then be credited to the capital account.
16. Current year earnings
The equity-based account type known as "Current Year Yearning" is used to reflect the net profit and loss for the current fiscal year on the balance sheet. The earnings for the current year will also be impacted by sales or any other transaction that has an impact on the income and expense account. The balance sheet will also include a mention of this.
Accounting and Business Administration-Advanced Certificate
designed to provide the learners with the required knowledge and hands-on skills needed to compete in the job market.
Account Ledger
An account or record that can handle bookkeeping entries for balance sheet and income statement transactions, like opening and closing balance in debit or credit, is known as a ledger. This sort of book or digital record includes detailed transaction information and bookkeeping entries, such as bank or cash transactions, stock value, customer billing, vendor invoice records, salary expenses, and many more. The ledgers provide all the necessary data needed to create financial statements.
Every transaction has a reference number that will help them understand the justifications and steps involved in carrying out that particular transaction.
The following are the many account ledgers available in Odoo 16:
1. Income account
2. Expense account
3. Stock input account
4. Stock output account
5. Stock valuation account
6. Price difference account
7. Account Receivable
8. Account Payable
9. Fixed Asset Account
10. Depreciation Account
11. Revenue Account
12. Deferred revenue account
13. Expense account
14. Deferred Expense Account
15. Bank Suspense Account
16. Outstanding Receipts Account
17. Outstanding Payments Account
18. Internal Transfer Accounts
19. Cash Discount Loss Account
20. Cash Discount Gain Account
21. Foreign Exchange Gain Account
22. Foreign Exchange Loss Account
Journals
Journals are key and essential records containing important data and information about a business's transactions according to the date on which the transaction was completed. Account Names, Date, Amount, and even whether the transaction is recorded as a debit or credit are all shown in great detail.
You may see pre-configured journals that are appropriate for practically all sectors using Odoo16 Accounting. Additionally, if necessary, the platform lets you define new journals. Five different types of journals are available on the Odoo16 platform to display similar types of transactions in a single journal. The five journal types in Odoo16 can be listed as follows when we list them.
● Sales
● Purchase
● Bank
● Cash
● Miscellaneous.
1. Sales Journal
Every single sales-related transaction is documented in the sales journal type. You can set up various sales journals according to your needs using the Odoo platform. You can record transaction details for sales from wholesale and retail separately, for instance, if that is what is necessary. The customer invoices will be recorded here.
2. Purchase Journal
To compile all transactions related to purchases, use the Purchase journal record. Different buy journals can be made to post received vendor bills, just like with sales journals.
3. Bank Journal
The Bank Journal keeps detailed records of every bank transaction. You may successfully track customer bank payments, vendor bank payments, and any other transaction recorded by your associated bank account by posting your bank statements.
4. Cash Journal
Now, we can document all cash transactions in a cash journal. This type of journal can record daily cash transactions and petty cash transactions, and it can also keep track of information about cash payments from customers.
5. Miscellaneous Journal
The final form of the journal is a Miscellaneous journal, which is excellent for recording transactions that are not covered by the four journals we previously discussed (Sales, Purchase, Bank, and Cash). The journal type can take into account many other entries that don't fit into the other four journal types, such as inventory value, inventory changes, exchange difference, opening balance, and many others. Even for a salary or all of your corrections, posting a journal type entry is quite convenient. There are no advanced settings available in the Miscellaneous journals.
These five journal kinds can each have a sequence number set up on the Odoo17 platform for convenience
Journals
Journals are key and essential records containing important data and information about a business's transactions according to the date on which the transaction was completed. Account Names, Date, Amount, and even whether the transaction is recorded as a debit or credit are all shown in great detail.
You may see pre-configured journals that are appropriate for practically all sectors using Odoo16 Accounting. Additionally, if necessary, the platform lets you define new journals. Five different types of journals are available on the Odoo16 platform to display similar types of transactions in a single journal. The five journal types in Odoo16 can be listed as follows when we list them.
● Sales
● Purchase
● Bank
● Cash
● Miscellaneous.
1. Sales Journal
Every single sales-related transaction is documented in the sales journal type. You can set up various sales journals according to your needs using the Odoo platform. You can record transaction details for sales from wholesale and retail separately, for instance, if that is what is necessary. The customer invoices will be recorded here.
2. Purchase Journal
To compile all transactions related to purchases, use the Purchase journal record. Different buy journals can be made to post received vendor bills, just like with sales journals.
3. Bank Journal
The Bank Journal keeps detailed records of every bank transaction. You may successfully track customer bank payments, vendor bank payments, and any other transaction recorded by your associated bank account by posting your bank statements.
4. Cash Journal
Now, we can document all cash transactions in a cash journal. This type of journal can record daily cash transactions and petty cash transactions, and it can also keep track of information about cash payments from customers.
5. Miscellaneous Journal
The final form of the journal is a Miscellaneous journal, which is excellent for recording transactions that are not covered by the four journals we previously discussed (Sales, Purchase, Bank, and Cash). The journal type can take into account many other entries that don't fit into the other four journal types, such as inventory value, inventory changes, exchange difference, opening balance, and many others. Even for a salary or all of your corrections, posting a journal type entry is quite convenient. There are no advanced settings available in the Miscellaneous journals.
These five journal kinds can each have a sequence number set up on the Odoo17 platform for convenience.
Accounting and Business Administration-Advanced Certificate
designed to provide the learners with the required knowledge and hands-on skills needed to compete in the job market.
Types of Accounting in Odoo 17
Odoo 17 primarily concentrates on three kinds of accounting practices. Accounting can be divided into two categories: "Anglo-Saxon accounting" and "Continental Accounting."
Odoo launched Storno Accounting, which employs negative credit/debit values for reverse entries.
Continental Accounting
The Odoo system and continental accounting, which is the most widely practiced accounting, and Odoo17 strongly support these ideas. This accounting practice is available both in the Enterprise and Community edition of Odoo 17. When making a purchase, this accounting will have an influence on the expense account. As soon as a product is found in stock, the expense of that item is therefore taken into account. Continental accounting is used by the Odoo17 platform by default. The stock can also be manually or automatically validated. The stock is unaffected if it is done manually, but the information must be manually posted at the end of each month or year.
Select the "Automated" inventory valuation technique if the stock valuations must be recorded as the stock is taken in and taken out.
Numerous beneficial effects of Continental accounting's long history can be seen in your company's accounting. Consequently, we may examine how various transactions or procedures in continental accounting are impacted by the ledgers.
Transactions in Continental Accounting
The financial activity that has a direct impact on a company's financial situation and financial statements is known as an accounting transaction. Basically, we may include any kind of money exchange under this category. These transactions are handled differently by different organizations or companies. So that we can examine some of the fundamental accounting transactions.
1. Purchase Process
The financial transactions that are necessary for the business to buy the goods or services needed to generate sales are referred to as purchases. All transactions related to purchases are referred to as "purchase journals" on the Odoo17 platform. The purchase voucher contains a record of all these transactions related to purchases. It is the transaction handled by the seller of a good or service bought, and it could even be a good or service bought, as well as any other asset bought. An entire series of transactions, including purchase order, material receipt, rejection out, purchase invoice, and purchase return, are included in a purchase.
Purchase Order: An official document produced by a buyer committing to pay the seller for the sale of a specific good or service that will be provided in the future is known as a purchase order. For the required sum, a buy order can be made for any products or services from a vendor. The beginning of a purchase order does not immediately affect the ledgers for either stock or accounts.
Material Receipt: The next operation is called Material receipt, and it deals with details like product quantities and lot numbers in regard to the goods that are intended for the employees' on-site job. The inventory item must be received and added to the inventory if the supplier supplies the product. The inventory will be updated with the quantities. Therefore, only the stock accounts are impacted by Material Receipt.
The "Stock Valuation Account" and "Stock Input Account" in the Odoo17 platform are impacted when the product is received.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stock valuation account | Asset | Increasing | Debit |
| Stock Input account | Liability | Increasing | Credit |
Rejection Out (Purchase Return): The organization frequently returns the products it has purchased even before making the payment. It might be for any cause. The product will be rejected if it becomes damaged. Similar to how there will be several factors involved in the rejection. The stock will consequently reverse. In this instance, only the stock will be impacted; the accounts won't change. The stock value will likewise drop as a result.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stock valuation account | Asset | Decreasing | Credit |
| Stock Input account | Liability | Decreasing | Debit |
Purchase Bill Creation: The payable account and the expense account will be impacted if you create a bill for the purchase order. Due to the fact that the payable account's nature is "Liability," it will be credited. On the other hand, because the expense account is an "expense" account, it is debited.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Account Payable | Liability | Increasing | Credit |
| Expense Account | Expense | Increasing | Debit |
Registering Payment: The payable account and the outstanding receipt account are both impacted when you generate a payment. The liability will be reduced if the payment has been made. Consequently, a debit will be made from the payable account. In the bank and cash journals of Odoo 17, a temporary account called outstanding payments is used to store unreconciled inputs. The kind of outstanding payment is "Asset." Therefore, the outstanding payment account is credited as the assets decrease.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accounts payable | Liability | Decreasing | Debit |
| Outstanding Payments | Liability | Decreasing | Credit |
Reconciling: The sum will be transferred to the bank account after it is compared or reconciled to the bank statement. As a result, the account for outstanding payments is debited, and the bank is given credit.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outstanding Payments | Liability | Decreasing | Debit |
| Bank Account | Asset | Decreasing | Credit |
The term "purchase return" refers to when a customer returns a product to a seller for a refund, store credit, or any other reason based on the seller's duty. The occasional return of a purchase will also happen. For instance, if the buyer is dissatisfied with the product, if they purchased it in error, if the merchant sent them the incorrect product, or even if they purchased more products than they actually needed. When a purchase is returned, the stock is reduced, and the paid amount needs to be refunded because it occurs after the invoice. Therefore, both the stock accounts and the accounts will be impacted by the purchase return. Reverse journal entries that are appropriate should be created to make up for this.
The table below lists each purchase transaction's journal entries in detail.
| Operation | Accounts Affected | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purchase order | No Accounts Affected | ||
| Material Receipt | Stock Valuation Account | XX | |
| Stock Interim Account | XX | ||
| Purchase Bill | Expense Account | XX | |
| Account Payable | XX | ||
| Registering Payment | Account Payable | XX | |
| Outstanding Payments | XX | ||
| Reconciling | Outstanding Payments | XX | |
| Bank Account | XX |
2. Sales Process
Sales transactions include any sale, contract, or other transfers that include the disposal of goods, services, or other assets, both tangible and intangible. Here, we may talk about how the Odoo17 platform can help you handle sales transactions, the operations that go along with them, and how that affects the journal entries. Operations like Sales Orders, Delivery Notes, Rejection IN (Sales Return), Sales Invoices, and Invoice payment are all part of a sales transaction. We might start by examining the following operations of sales transactions.
Sales Order: A sale order is essentially a document created by the seller to gather details regarding the goods or services the customer has requested. Every detail is included in the sales order, including information on the product or service, the price, the quantity, the terms and conditions, and many other things. The selling order is, therefore, solely intended for the creation of orders since it has no effect on inventories or accounts.
Delivery Note: An element connected to the shipment or delivery of goods is a delivery note. This will include the specifics of the goods, how many there are, and how much they cost. Dispatch Note and Goods Received Note are other names for the Delivery Note. The stock value reduces as a confirmed order is fulfilled from the inventory and delivered to the customer. Two accounts, the "Stock Valuation Account" and the "Stock Output Account," are impacted by the delivery of goods to customers.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stock valuation account | Asset | Decreasing | Credit |
| Stock Output account | Liability | Decreasing | Debit |
Rejection IN (Sales Return): Numerous times, buyers return products even after being billed. Adjustments are made to stock and accounts as a result of this form of sales return. They will also have reverse journal entries created for them. For keeping track of the products that customers have rejected or returned, a Rejection IN is a very helpful feature. If the goods are returned prior to billing, just the stock will be impacted; the accounts are unaffected. Additionally, the stock value rises when the product is added back to the inventory.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stock valuation account | Asset | Increasing | Debit |
| Stock Output account | Liability | Increasing | Credit |
Sales Invoice Creation: A type of accounting document called a sales invoice is sent to a buyer by a vendor of products or services. Everything will be mentioned, including the service provided, the product provided, the price the buyer must pay, the mode of payment, and more. It is necessary for bigger transactions and is a legally binding agreement between the company and the customers.
Both the Receivables Account and the Income Account will be impacted in this situation. The Account Receivable is labeled as an "Asset," and the Income Account is labeled "Income" when we analyze the characteristics of these accounts. In this instance, the revenue is rising while the asset is decreasing. As a result, the Income Account is debited, and the Account Receivable is credited.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Income Account | Income | Increasing | Credit |
| Account Receivable | Asset | Increasing | Debit |
Registering Payment: On payment registration, a temporary account called Outstanding Receipts is used. Due to payment registration, a journal entry is produced with Accounts Receivable and Outstanding Receipts.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accounts Receivable | Asset | Decreasing | Credit |
| Outstanding Receipts | Asset | Increasing | Debit |
Reconciliation: After reconciliation, the sum will be transferred to the bank account after it is compared to the bank statement. As a result, the bank is debited, and the account for outstanding receipts is credited.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outstanding Receipts | Asset | Decreasing | Credit |
| Bank account | No Accounts affected |
You can see a breakdown of all the sales transactions' journal entries by looking at the table below.
| Operation | Accounts Affected | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales order | No Accounts affected | ||
| Delivery Note | Stock valuation account | XX | |
| Stock valuation account | XX | ||
| Customer Invoice | Income Account | XX | |
| Account Receivable | XX | ||
| Registering Payment | Accounts Receivable | XX | |
| Outstanding Receipts | XX | ||
| Reconciling | Outstanding Receipts | XX | |
| Bank Account | XX |
Finally, using the double-entry bookkeeping method, the total of the credits will equal the total of the debits.
Accounting and Business Administration-Advanced Certificate
designed to provide the learners with the required knowledge and hands-on skills needed to compete in the job market.
Anglo-Saxon Accounting
For tiny areas, such as those found in the United States, United Kingdom, Ireland, Canada, Australia, and many other nations, Anglo-Saxon Accounting is applicable. Odoo17 only offers Anglo-Saxon accounting in the enterprise edition. There are numerous contrasts between the two accounting systems, Continental and Anglo-Saxon. We talked about how a purchase affects the expense account in Continental Accounting. However, in Anglo-Saxon accounting, after executing a sale order has an impact on the expense account.
You must enable Anglosaxon accounting from the Odoo Accounting Configuration Settings if you wish to use all of its features, and you should activate the developer mode. The cost distinctions between Account and Stock account properties when the inventory valuation is automated is another important aspect of the Anglo-Saxon accounting system. To track the price difference between the vendor bill and the purchase cost, use the price difference account.
Transactions in Anglo-Saxon Accounting
1. Purchase Process
In some cases, the expense won't register when it is made. The purchases could be made in bulk and consumed over a lengthy period of time. Therefore, including them as an expense in financial entries will have a bigger effect on the company's profit and loss. It is, therefore, common practice to record acquired products as assets and costs at the moment of use in order to handle those scenarios. Ledgers contain the cost of spent assets.
We will start by making a product purchase.
Purchase Order: Purchase orders do not impact any accounting ledgers; they just produce a valid document for receiving products or services from the vendor.
Purchase Receipt: After the goods' receipt has been acknowledged, the arriving assets must be added to stock. As a result, both stock input accounts and stock valuation accounts are impacted by stock.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stock valuation account | Asset | Increasing | Debit |
| Stock Input account | Asset | Decreasing | Credit |
When stock is received and recorded in the "Stock input account," it is thought of as an asset until it is sold or consumed at which point it becomes a liability. So, it might be either assets or liabilities. [Liability = -Assets] as either the liability or the asset changes.
Purchase Return: There is occasionally a chance that the purchased item can be returned because of a quality problem or product damage. As a result, stock accounts are reversed, and the stock move is exactly the opposite of the incoming.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stock Valuation Account | Asset | Decreasing | Credit |
| Stock Input Account | Asset | Increasing | Debit |
Purchase Bill:Posting the purchase bill follows completion of the purchase receipt. As was already indicated, in Anglo-Saxon, the direct expense will be recorded as an asset rather than at the time of purchase. As a result, once a bill is generated, "Account Payable" and "Stock interim accounts" are impacted. The amount to be paid to the vendor is noted in Account Payable. As a result, when a bill is generated, the amount owed to the vendor rises, increasing the company's liability and crediting the Account Payable.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Account Payable | Liability | Increasing | Credit |
| Tax Account | Asset | Increasing | Debit |
| Stock Input account | Asset | Increasing | Credit Or Debit |
Register Payment: Making a payment or sending money to the vendor is known as registering it. 'Account Payable' and 'Outstanding Payment Accounts' are impacted by this process. The company's liability decreases as a result of payments made to the vendor. The company's payable liabilities are recorded in account payable. As a result, Account Payable, which by definition is a liability, is debited when the liability diminishes.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accounts Payable | Liability | Decreasing | Debit |
| Outstanding Payments | Liability | Increasing | Credit |
The Outstanding Payment account serves as a middleman for holding unreconciled outbound payments alongside cash and bank journals. Rather than using the Account Payable, these outstanding payment accounts are used to reconcile with the bank statement. As a result, whenever a payment is registered, the "Outstanding Payments" account is credited.
Reconciliation: The bank statement and vendor payment must match because that is the next step. The 'Outstanding Payment' and 'Bank' accounts are thus impacted by reconciliation.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outstanding Payments | Liability | Decreasing | Debit |
| Bank Account | Asset | Decreasing | Credit |
During this procedure, it will be noted that the vendor has finally received payment from the bank account. As a result, the asset in "Bank" decreases, which credits "Bank," and the liability in "Outstanding Payment" reduces, which debits "Outstanding Payment."
The table below displays the total journal entries made during the buying process.
| Operation | Accounts Affected | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purchase order | No Accounts Affected | ||
| Material Receipt | Stock Valuation Account | XX | |
| Stock Valuation Account | XX | ||
| Purchase Bill | Stock Valuation Account | XX | |
| Account Payable | XX | ||
| Tax Account | XX | ||
| Registering Payment | Account Payable | ||
| Outstanding Payments | XX | ||
| Reconciling | Outstanding Payments | XX | |
| Bank Account | XX |
2. Sales Process
The sales transaction entails a number of procedures, including the establishment of the order, the handling of the product delivery to the customer, the generation of the invoice, as well as its payment and reconciliation.
Sale Order: A sales order is made when a customer specifies the goods and services they need, the quantity they need, the confirmed pricing, etc. There is no impact on any accounts.
Delivery Note: After an order is accepted, the items must be delivered to the consumer. The attributes of the stock account will change once delivery has been authenticated. The stock that was supplied to the customer is tracked in the "Stock Output Account." A "Stock Output Account" is an expense by nature, and in this case, the expense value rises and is debited. Additionally, the value of all the stock or assets in the warehouse declines and is recorded in the "Stock Valuation Account." So, a credit is made to the stock valuation account.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stock Valuation Account | Asset | Decreasing | Credit |
| Stock Output Account | Expenses | Increasing | Debit |
Sales Return:Sales Return: Take into account a customer returning goods for any reason. In this manner, the stock is likewise inverted.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stock Valuation Account | Asset | Increasing | Debit |
| Stock Output Account | Expenses | Decreasing | Credit |
Sales Invoice: The 'Income Account' and 'Account Receivable' are impacted when creating a sales invoice for a customer. While "Account Receivable" refers to assets, "Income Account" refers to income. Thus, as assets grow and income rises, the "Income Account" is credited, and the "Account Receivable" is debited. Additionally, two other ledgers—the "Stock Output Account" and the "Expense" Account—are also impacted because, according to Anglo-Saxon accounting, the expense is impacted as soon as the acquired item is used up or sold out.
| Accounts | Nature | Increasing Or Decreasing | Credit Or Debit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Income Account | Income | Increasing | Credit |
| Account Receivable | Asset | Increasing | Debit |
| Tax Account | Liability | Increasing | Credit |
| Stock Output Account | Expenses | Decreasing | Credit |
| Expense Account | Expenses | Increasing | Debit |
Payment Registering: The 'Account Receivable' and 'Outstanding Receipts' accounts are impacted once payment has been received from the customer and has been registered in Odoo17.
Audit Reports
When it comes to business accounting, auditing is a critical component of finance management tasks. This unavoidable component is recognized as a priority throughout the fiscal periods that are now being formed. Furthermore, in compliance with requirements, the entire fiscal year's financial operations are checked, recorded, filed, and audited. This is normally done once every fiscal year. The Accounting module in Odoo provides you with specialized Audit Reporting features to help you manage your company's finances and oversee its accounting operations.
There is a distinct category of Audit Reporting tools available, including General Ledger, Trial Balance, Consolidated Journals, Tax Report, Intrastat Report, EC Sales List, and Journal Audits, all of which are accessible via the Odoo Accounting module's reporting page. Let us now go over each of the Audit reports separately in the next section.
General Ledger
All accounting data related to business operations will be defined in the company's general ledger. Furthermore, filters may be applied to Dynamic reports, and the General ledger displays all business transactions from all Account Ledgers used in the firm. All financial transactions connected to the company's sales, purchases, and other activities will be defined in a unique way here to help the viewer understand those transactions immediately. Furthermore, the well-organized menu may be utilized to study and identify specific information relevant to the company's financial management methods.
You may examine the company's general ledger by selecting the Reporting option in the Accounting module, as illustrated in the following screenshot. All of the financial operations items that have been filtered to appear for the given time will be displayed here. Every journal that has been posted will be explained, along with the invoice and bill details for that journal.
Additionally, you have the option to Print Preview, which will provide a General Ledger Report preview before printing. In addition to exporting General Ledger data, you may export the report in XLSX format for use in other corporate activities by selecting the Export (XLSX) option. The Save option ensures that the set details and filtering parameters are saved in the reporting menu. You may opt to enlarge a Journal, which will display all linked bills and invoices. The Ledger entries in the image below have been filtered to the month of January in the year 2024, and Sample has also been selected as the Journal filter. Furthermore, only the entries that have been uploaded are screened.
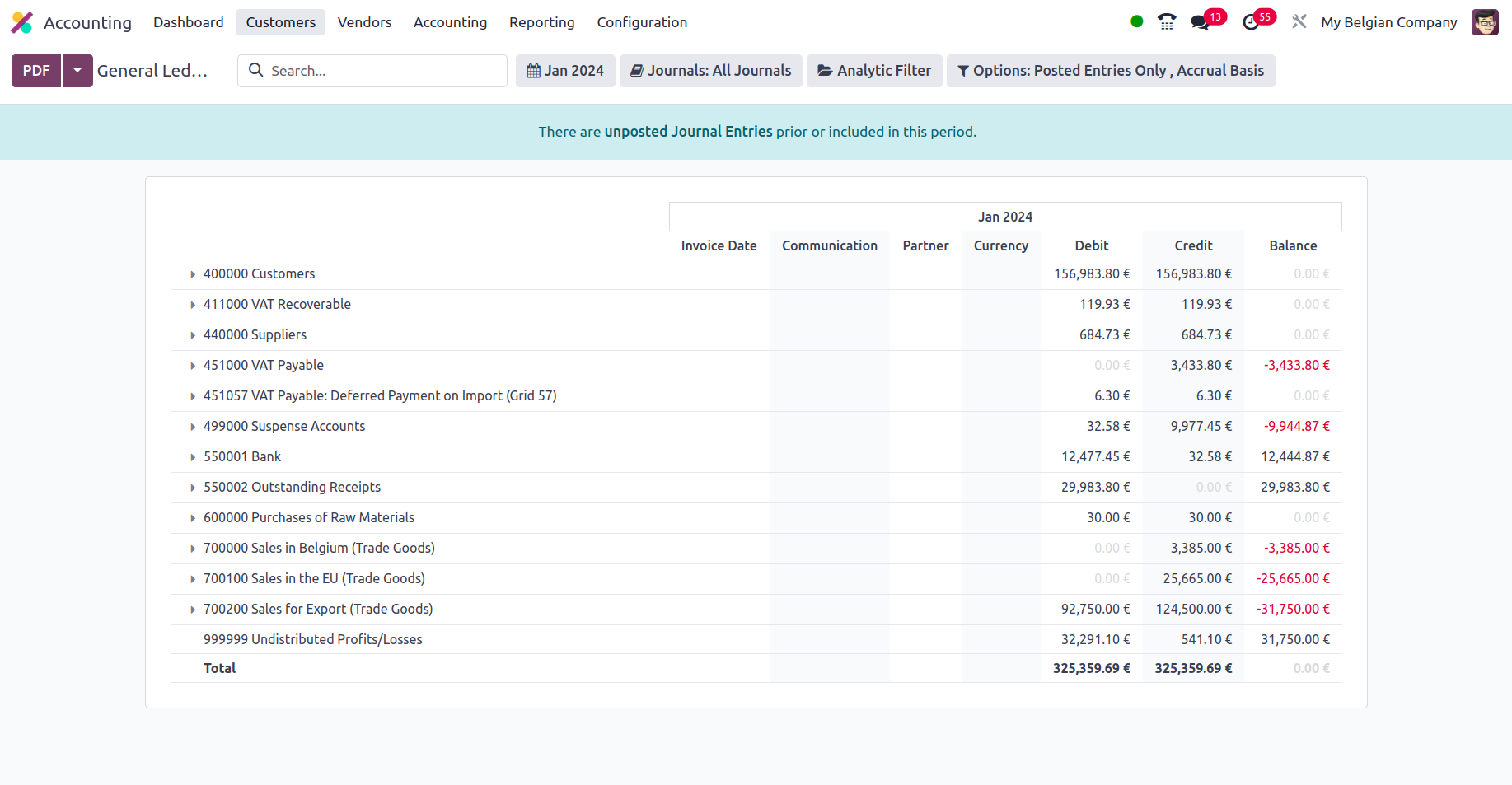
When an account is opened, the impacted journal entries are displayed together with the date, partner information, currency, debit/credit amount, and balance. Additionally, a right-click allows you to see and comment on the Journal Entries (add notes on each entry). The remarks made to the journal entries can be viewed and updated at the bottom of the General Ledger. You may filter the date or month of operations as This Month, This Quarter, This Financial Year, Last Month, Last Quarter, or Last Financial Year if you need to define a custom filter date of operations. The Filtration menu in the General Ledger menu is shown in the screenshot below.
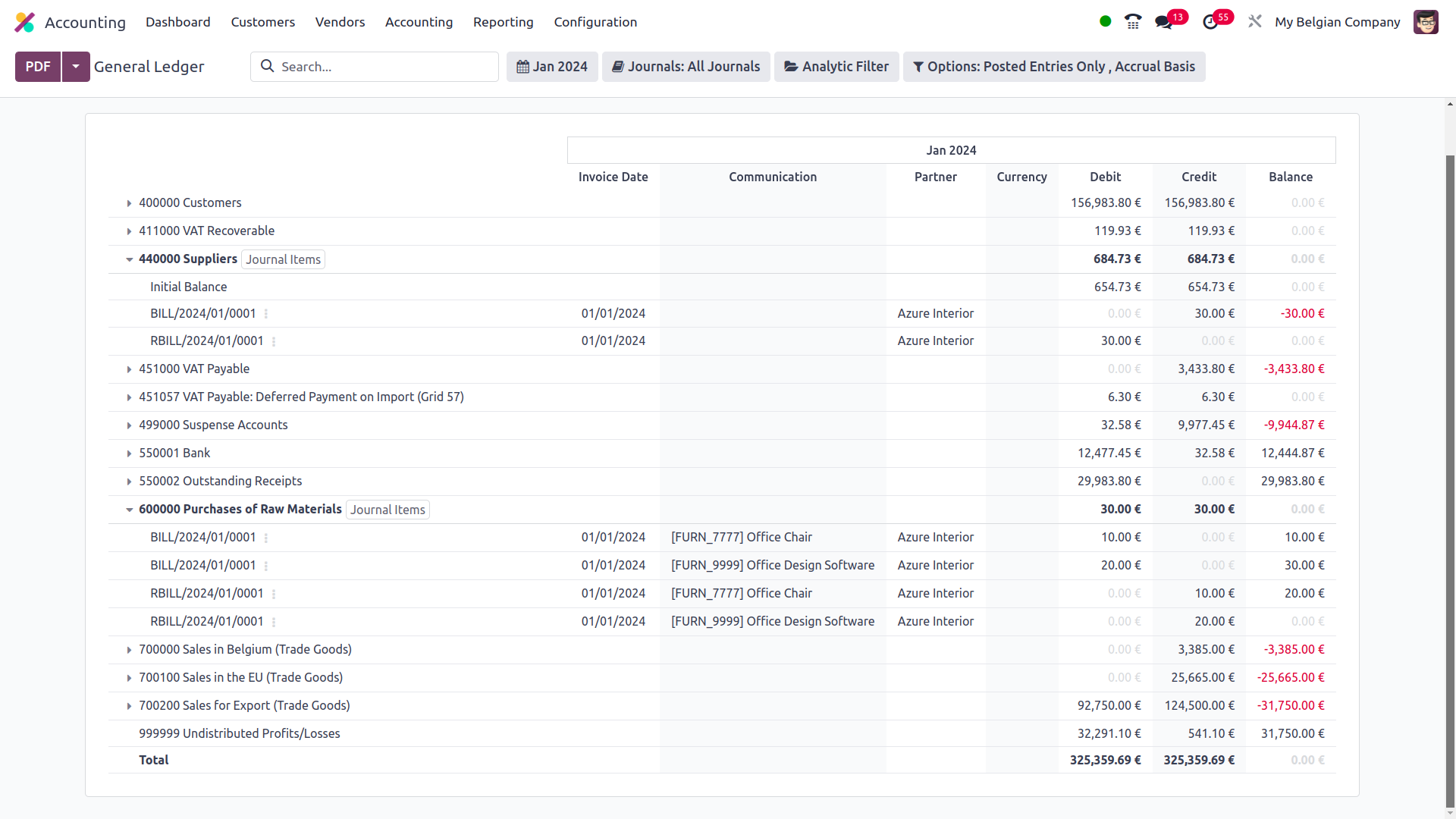
You have a different option to filter the journals where you can pick the particular journals to be filtered as well as the defined journal groupings that may also be selected as the filter.
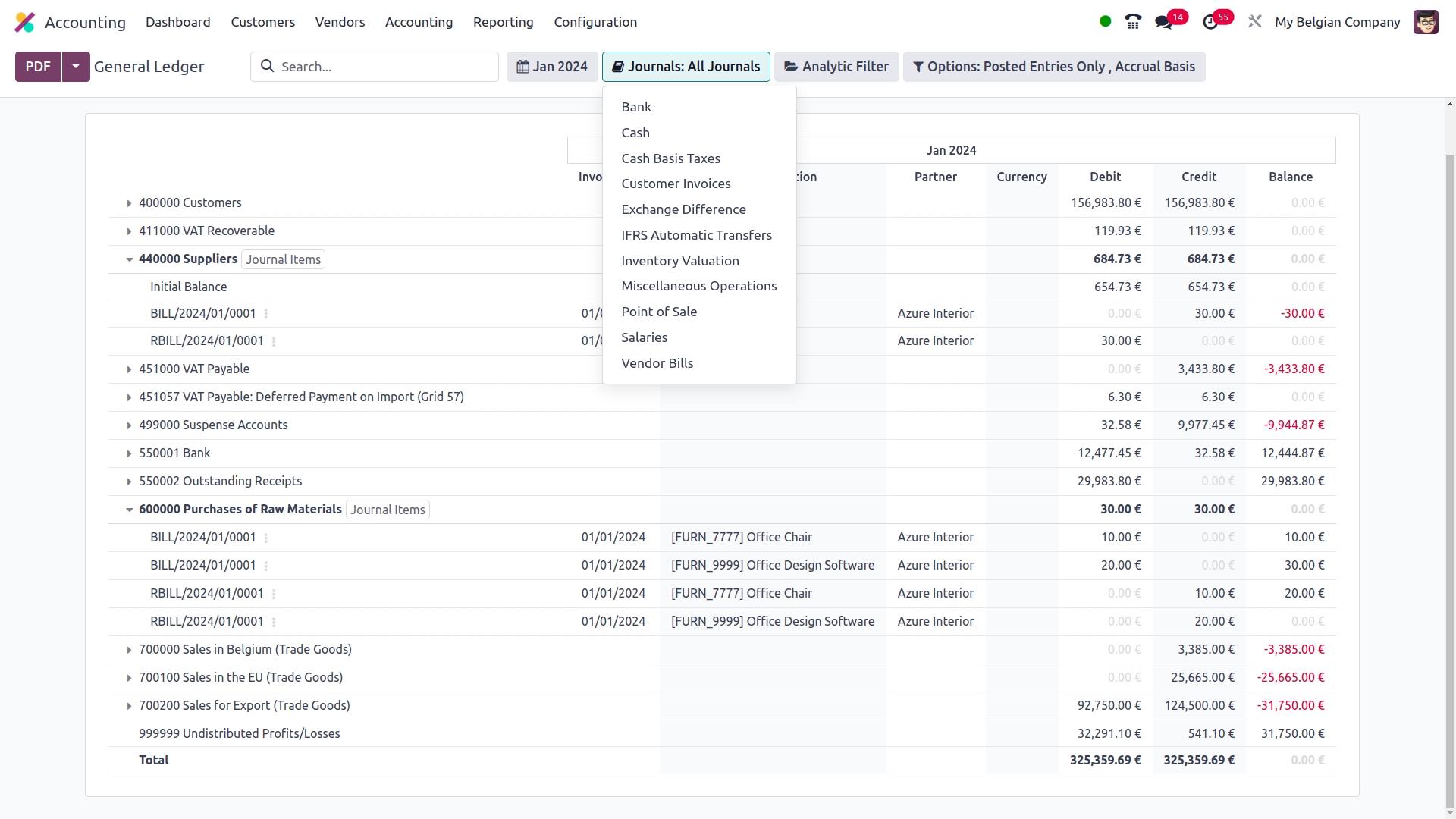
Additionally, using the available Analytic option, the filtration may be done in relation to the Analytical Accounting sections of the firm's financial management. Define the Analytical Accounts and Tags here to filter out General Ledger entries.
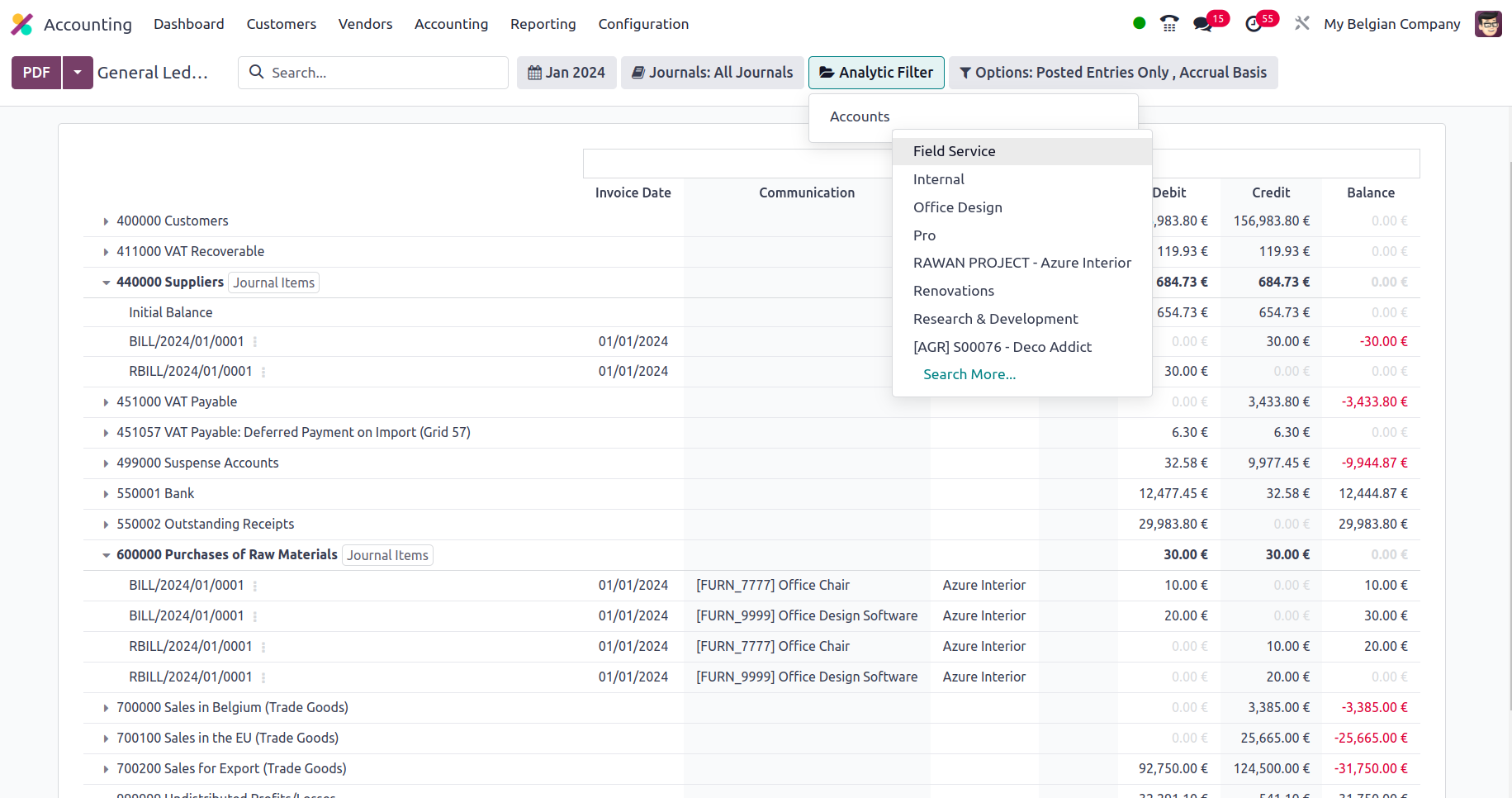
In addition, there is a particular filtering tool provided. This filter contains just Posted Entries by default, but it also offers the choices to Include Unposted Entries, Use Accrual Basis, Unfold All, and Use Cash Basis Method. Using this option, the required General Ledger entries can be defined in operation. There are also buttons that allow you to print reports in PDF and XLSX formats. The Store button saves reports to the proper place in the Documents modules, allowing you to keep financial information.
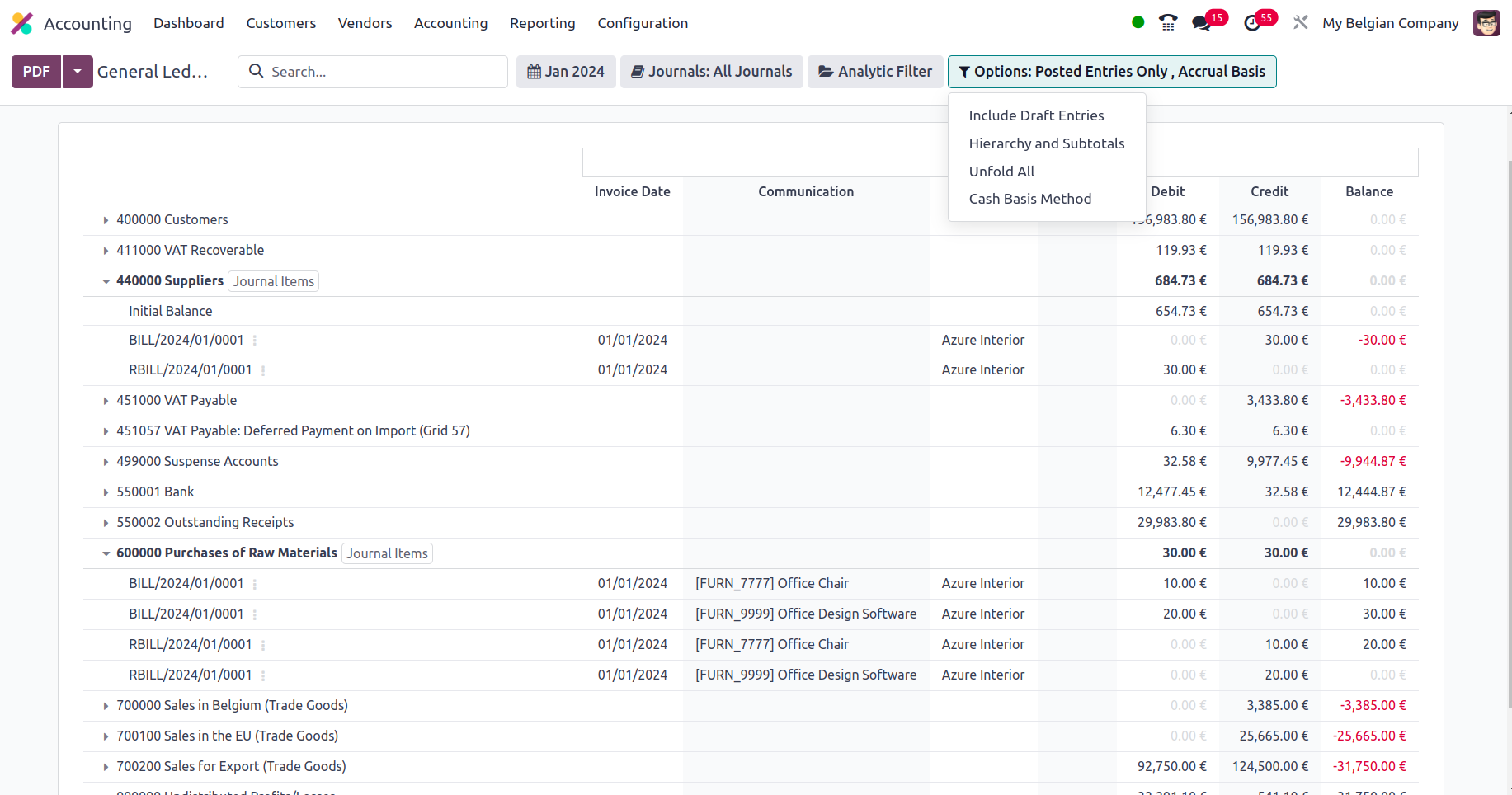
The general ledger is a report that initiates all posted and unposted accounting operations connected to the operation of the firm. In the early days of business, a specialized book known as General Ledger was kept, but with the Odoo Accounting module, all entries will be automatically displayed with regard to the corporate activities of the different Journals. Now that we've covered the Odoo Accounting module's General Ledger reporting menu, let's move on to the next section, which defines the Odoo Accounting module's Trial Balance Report.
Trial Balance
A trial balance is a sort of bookkeeping instrument that describes the balance of each account in credits and debits in terms of the organization's accounting activities. The Odoo Accounting module's specific Trial Balance reporting tool is specified in the module and available via the module's Reporting page. All filtered journals will be displayed in the Trial Balance report option, together with the operations' beginning balance information in the form of a debit and a credit. The Debits for the appropriate time will then be displayed, together with the Credit amounts of the entries, with the Total Debit and Credit Amount stated. You will also be able to search for a certain Account in the Trial Balance report.
There is also a Print Preview option, which displays a preview of the Trial Balance Report before it is printed. In addition to exporting the Trial Balance details, you may export the report in XLSX format for use in other business operations by selecting the Export (XLSX) option. The Save option saves the set details and filtering options in the reporting panel.
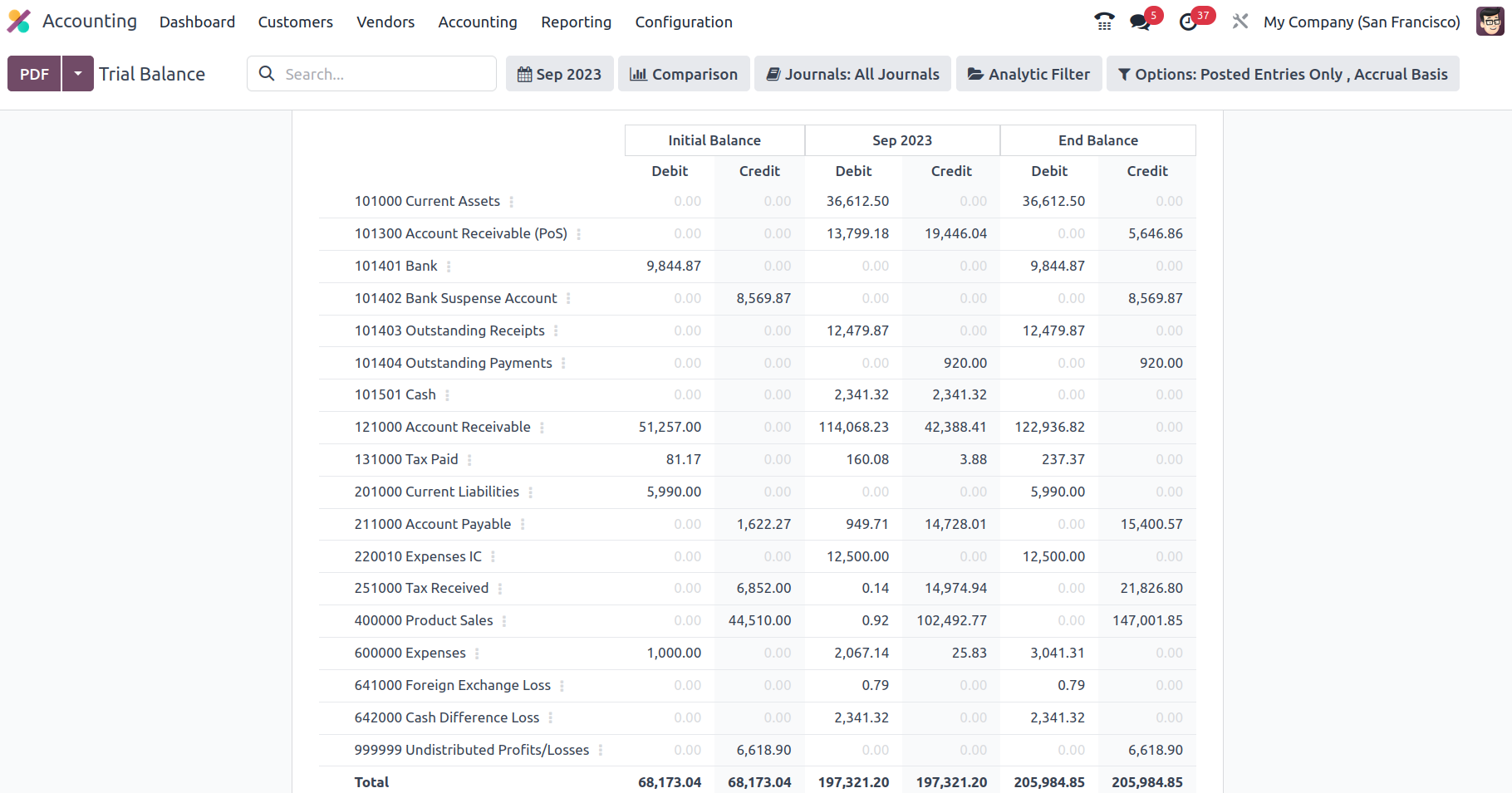
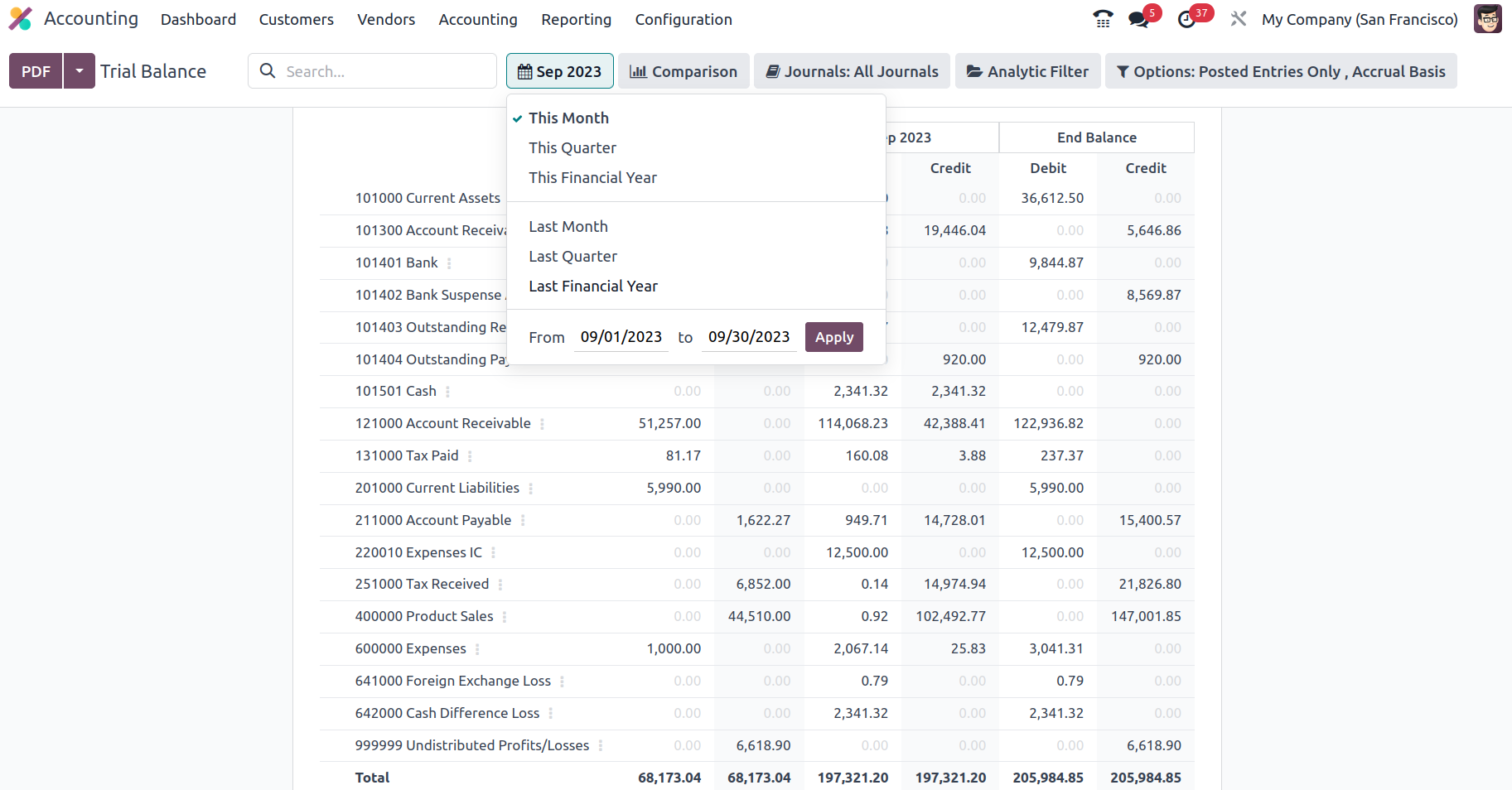
In terms of the Group by feature, you may define the Trial Balance for This Month, This Quarter, This Financial Year, Last Month, Last Quarter, and Last Financial Year, or add Custom filters as needed. The Group by choice is displayed in the accompanying snapshot, and they may be used to filter the Accounts depending on how long the firm has been in existence.
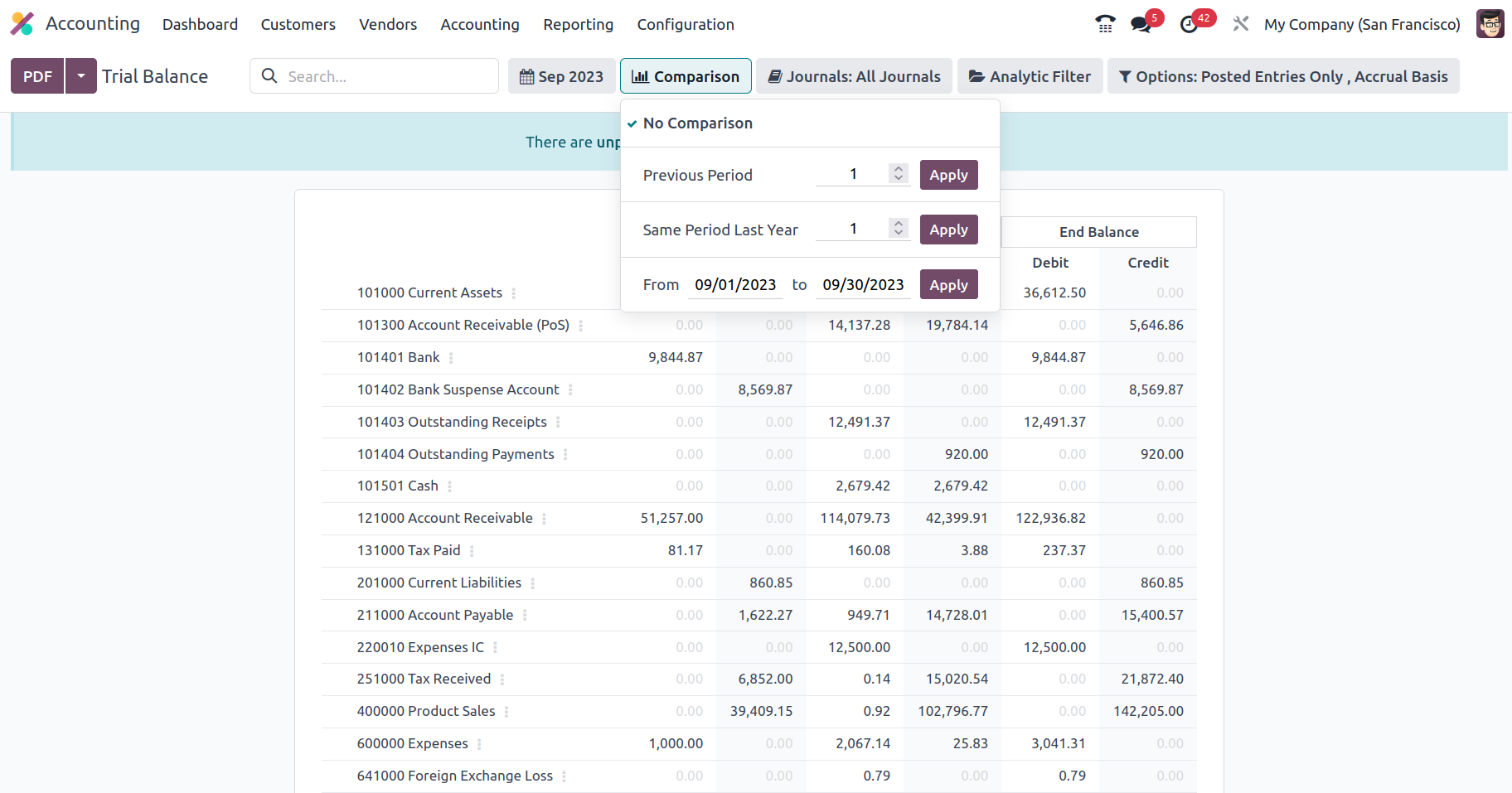
There is also an extra Comparison option that you may use to establish the comparison between the company's Journal entries. The comparison might be with the preceding period, the same period from the previous year, or a bespoke comparison set by the needs. Once the Comparison is created, the Trial Balance Report will specify the two Periods, the current one and the one you need to compare, as seen in the accompanying picture.
The Journal Groups and particular Journals given can also be used to group the Journals. If you employ this grouping approach, you will have a better understanding of the Trial Balance elements in relation to each of the operational Journals.
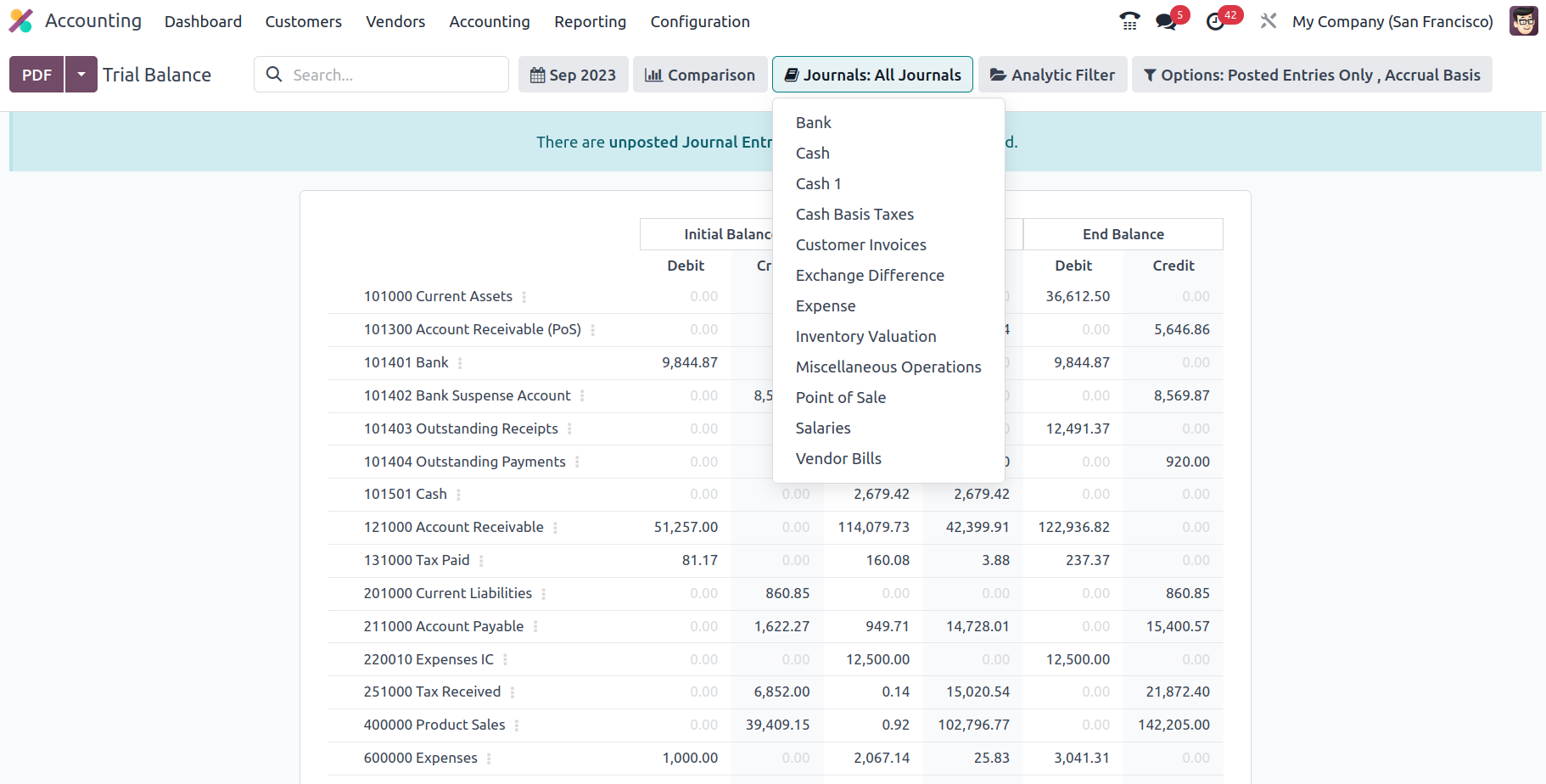
Additionally, the filtration may be done in reference to the Analytical Accounting sections of the company's financial management utilizing the available Analytic option. Define the Analytical Accounts and Tags below to filter the items in the Trial Balance report.
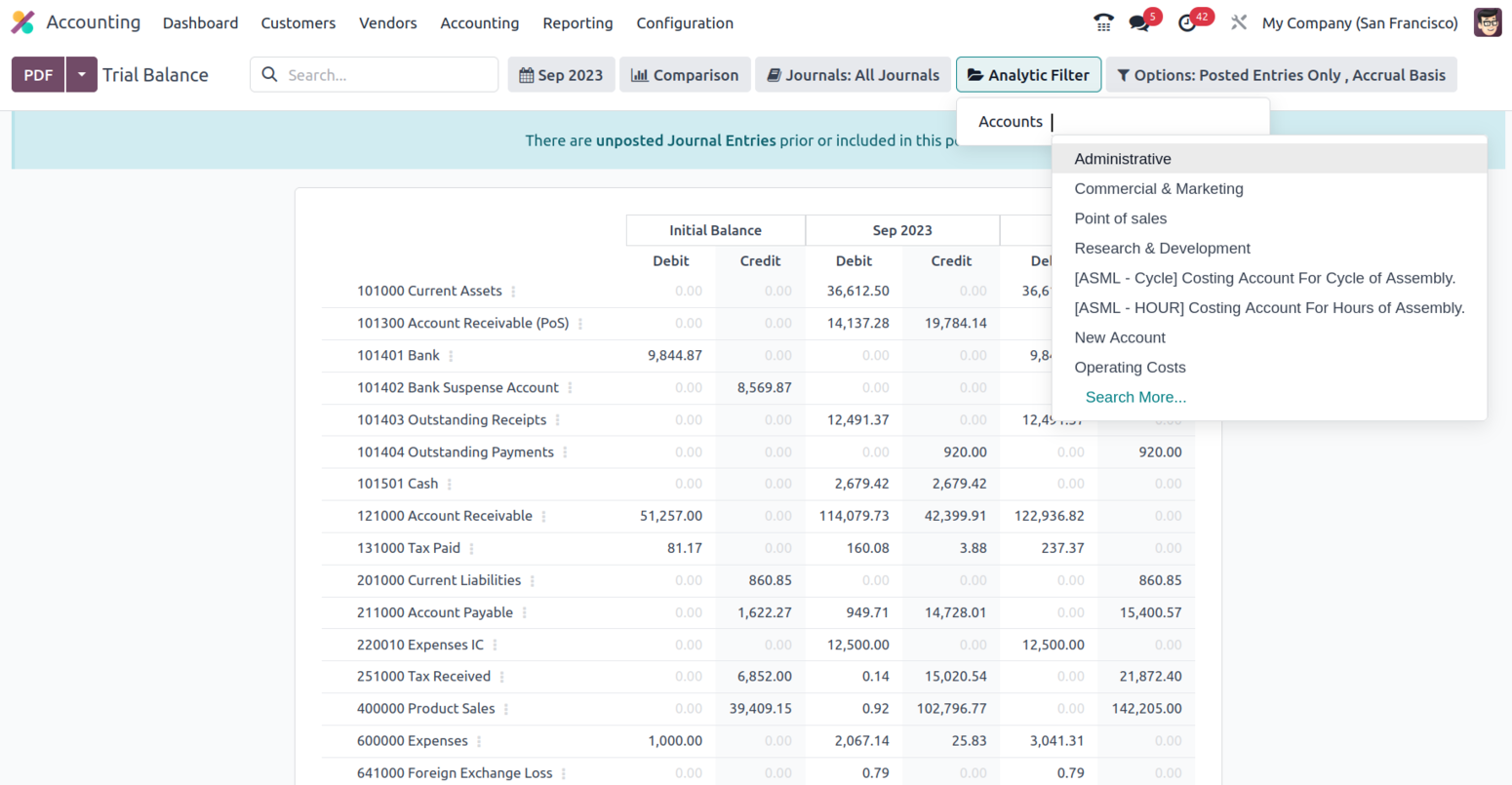
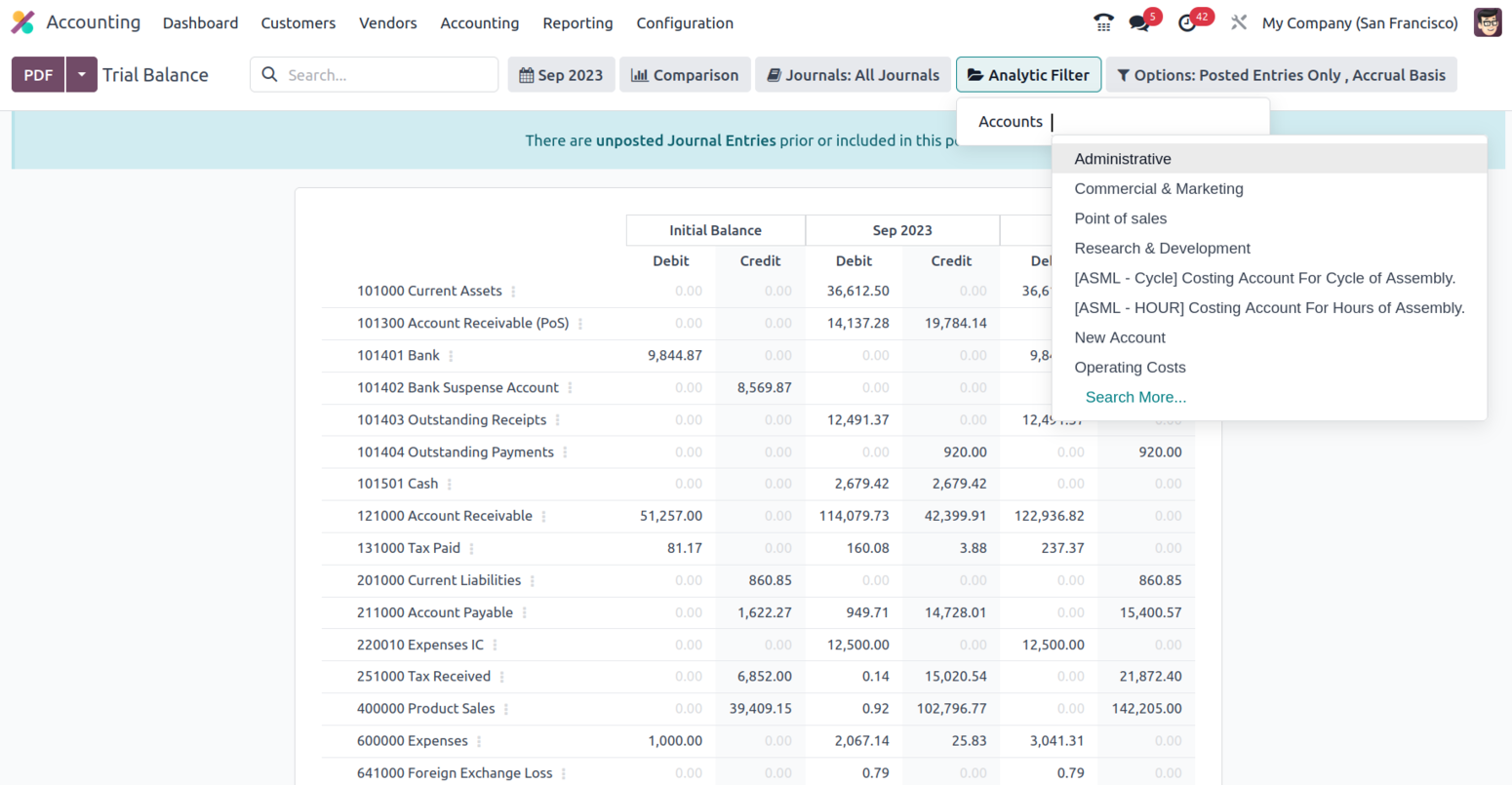
In addition, there is a particular filtering tool provided. This filter contains just Posted Entries by default, but it also offers the choices to Include Unposted Entries, Use Accrual Basis, Unfold All, and Use Cash Basis Method. Using this option, the necessary Trial Balance entries can be defined in operation. There are also buttons that allow you to print reports in PDF and XLSX formats. The Store button saves reports to the proper place in the Documents modules, allowing you to keep financial information.
The Trial Balance report of the company's financial activities will provide detailed information on the Credit and Debit amounts relevant to the organization's operations. The Trial Balance report will also be useful in grasping and gaining an overview of the company's financial activity. Let's move on to the part that defines Journal Reports in Odoo as they relate to the accounting process of the organization.
Journal Report
The journals of your accounting operations that are marked as Consolidated for the operations are defined in the Odoo Accounting module's Journal report menu. All operational Journals and their respective operating months will be presented in the menu. The Consolidated Journals report may also be produced as a preview by selecting Print Preview. Additionally, by selecting the Export (XSLX) option, the Consolidated Journals in the XLSX report may be exported. After filtering and aggregating the Consolidated Journals according to another setting element, you may store them to report using the Store option.
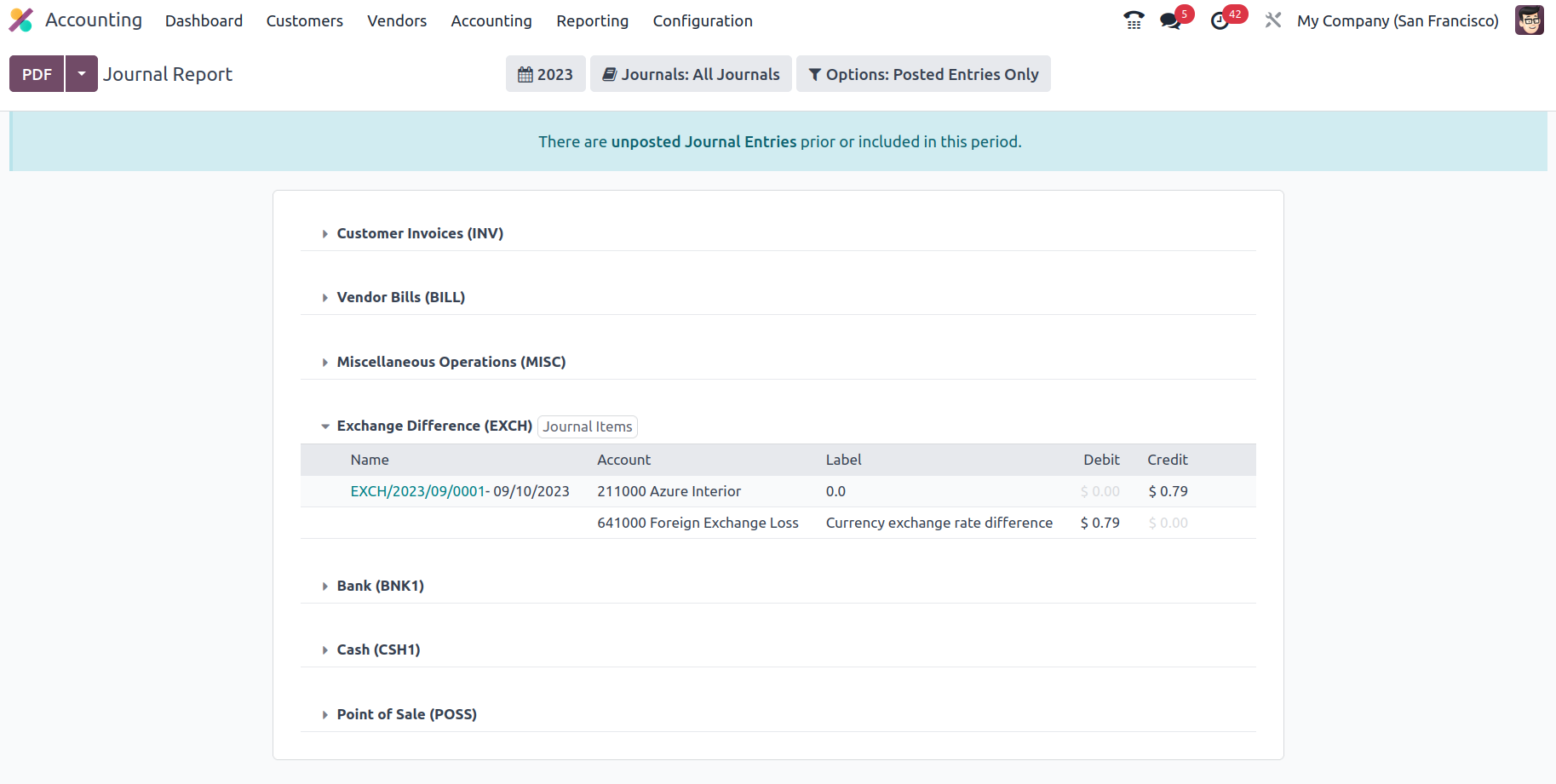
A tax declaration will also be added at the conclusion of the entries for sales and buy journals, as seen in the screenshot.
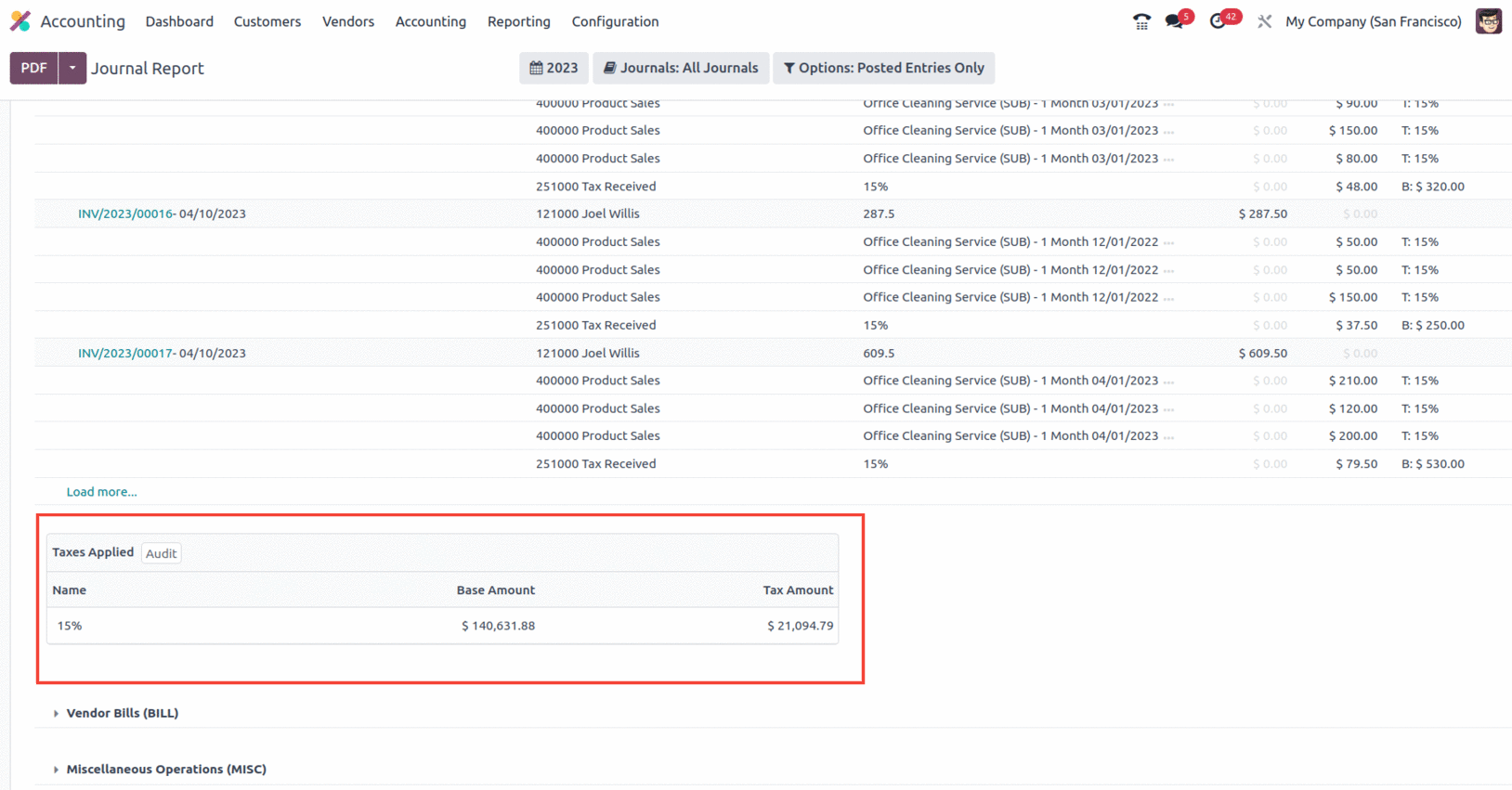
When it comes to sorting the entire depicted in the Consolidated Journals, you have the option to Group by options based on the period of the operation, as well as filtration options like This Month, This Quarter, This Financial Year, Last Month, Last Quarter, Last Financial Year, or add Custom filters of operations as needed. The Group by options available to you to filter the Accounts based on how long the business has been in operation are given in the screenshot below.
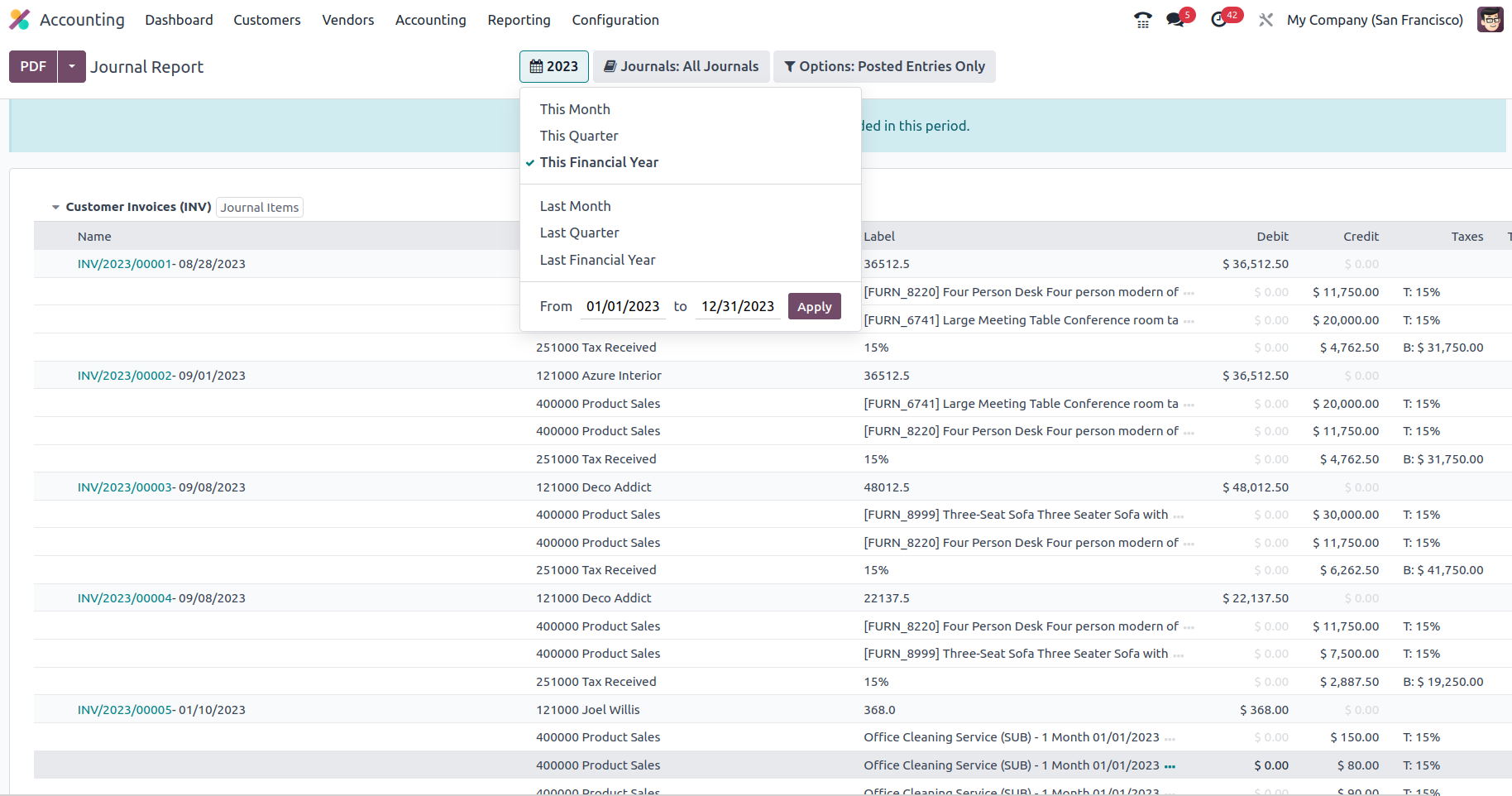
The Journal Groups and particular Journals given can also be used to group the Journals. Using this process of grouping by Journals, you may better understand the Consolidated Journals aspects in connection to each of the operational Journals being built.
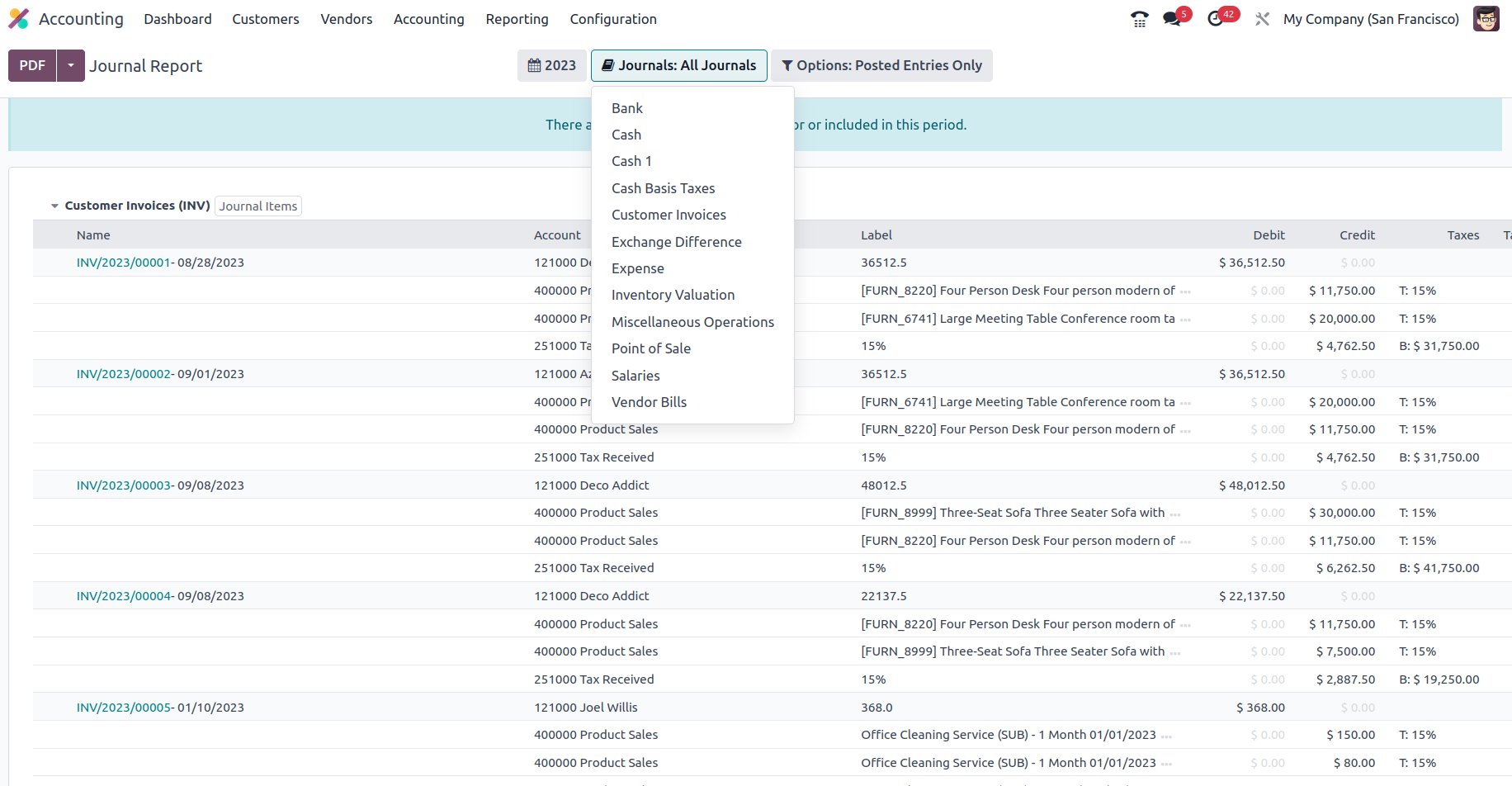
Additionally, the settings tool allows you to filter entries by utilising the Posted Entries Only, Include Unposted Entries, and Unfold All choices. Thanks to these filtering tools and selections, you will have clearly defined options for excluding and sorting the Consolidated Journals items.
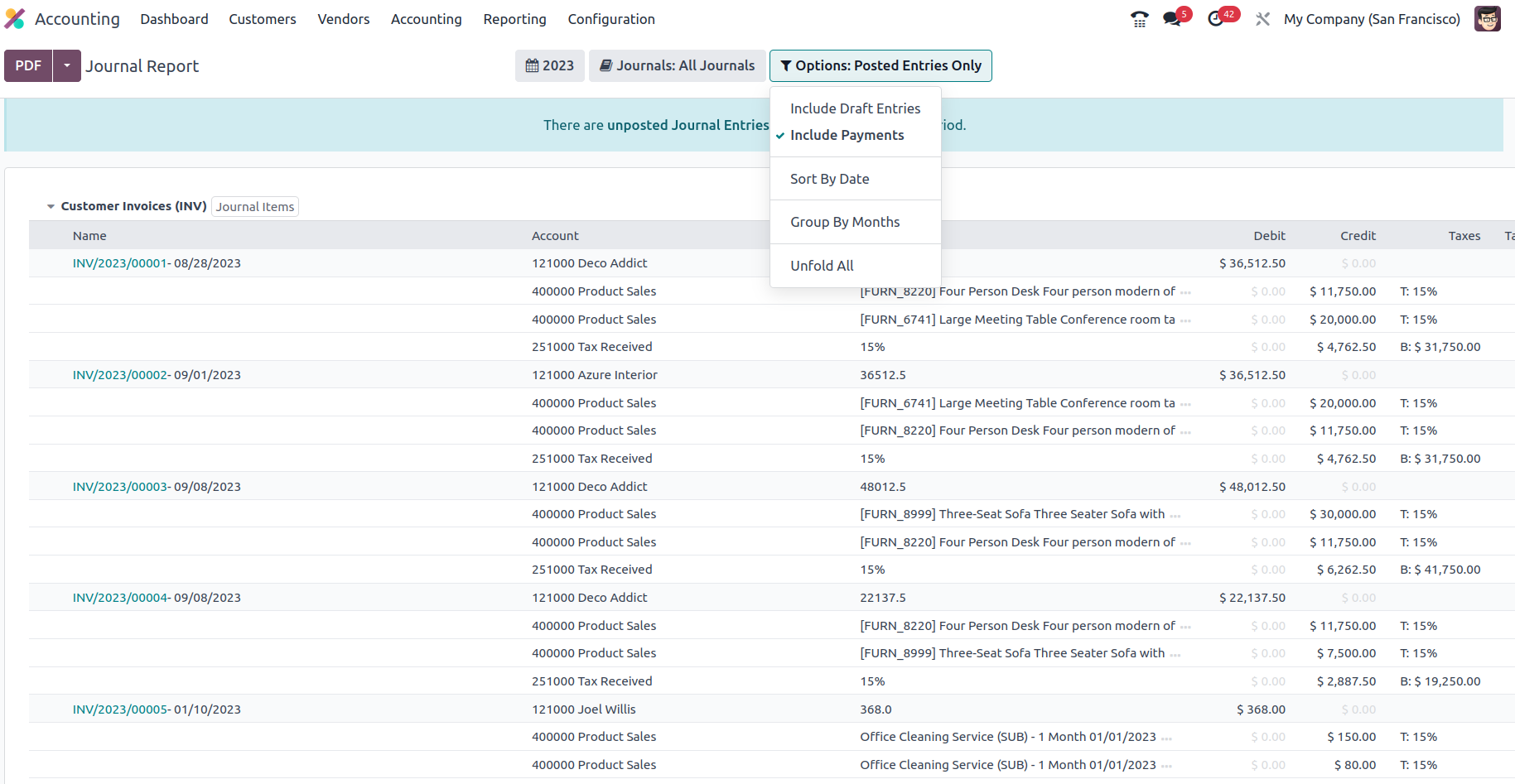
The Consolidated Journals reporting window ensures that the viewer understands all of the financial entries and their allocated components of the company's accounting activities. The Intrastat report, the next reporting tool in the Odoo Accounting module, will be discussed in the following portion of this chapter.
Intrastat Report
The Intrastat Report is one of the more comprehensive reporting options provided by Odoo's Accounting module. The European Union and its member states may track trade and business in a statistical manner owing to the Intrastat reporting mechanism. The Odoo Accounting module's Reporting tab leads to the Intrastat Report menu. This page will display all of the Intrastat Reporting components relating to business operations. There are further options in the menu for Group by and specialized Filtering that can aid in the sorting process.
Filtering tools will aid the Filtering component of the Intrastat Reports in the Odoo platform in relation to the Fiscal Periods of Operations, Journals that have been defined, Types of Journal Entries, and Filtrations depending on the Option as well as the Company in which Business is performed either as Partners, Vendors, or Customers.
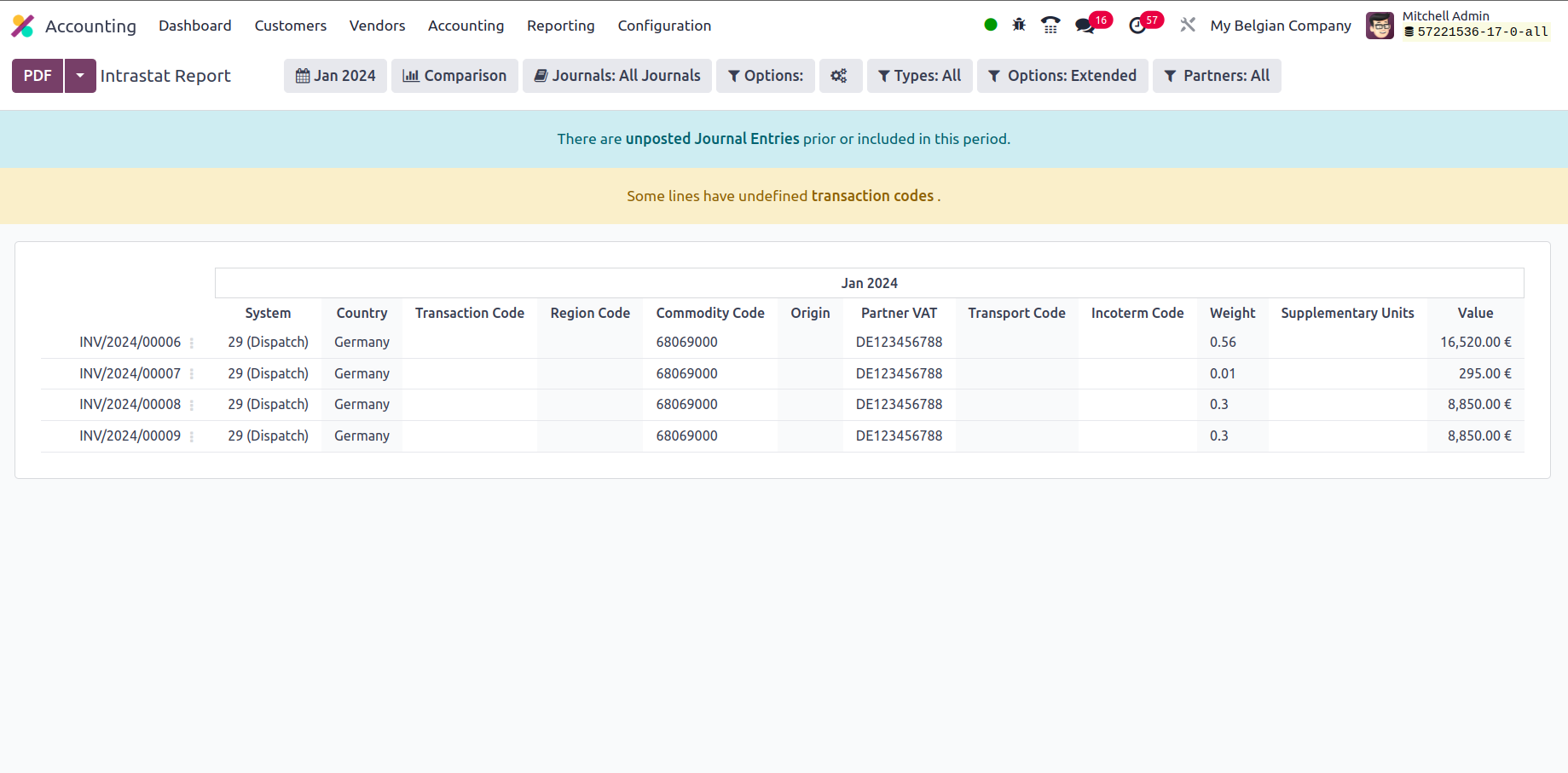
If you want to learn more about the filtration features of the entries mentioned in the report, you may refer to the reporting aspects provided in the preceding sections. There are also buttons that allow you to print reports in PDF and XLSX formats. The Store button saves reports to the proper place in the Documents modules, allowing you to keep financial information. Let us go to the next phase, where we will define the Odoo platform's EC Sales List reporting option.
Check Register
The Check Register option is the last one under the Audit Reporting tools in the Odoo Accounting module, and it will provide you with information about your company's Check Register. A check register will describe every financial transaction linked to the firm's functioning, and the check register report will do so analytically, providing you with a full insight into how everything works.
The Accounts Register report will be illustrated using the numerous working Charts of Accounts that have been established in the platform. Each operational Chart of Accounts, as well as the date of operation, communication information, partner, and currency utilized, will be noted here. Furthermore, the Debit and Credit amounts, as well as the Balance of each of the Charts of Accounts, will be described as shown in the following screenshot.
Filtering and grouping possibilities are accessible, much like any other reporting choices in the Odoo Accounting module. You may use the criteria below to narrow down the information in the cheque register based on fiscal periods, journals, analytical accounting features, and posted and unposted entries. There is also a serving tool that you may use to search the Bill Register entries depending on the data you have. There are also buttons for printing reports in PDF and XLSX formats. The Store button saves reports to the proper location in the Documents modules, allowing you to keep your financial information.
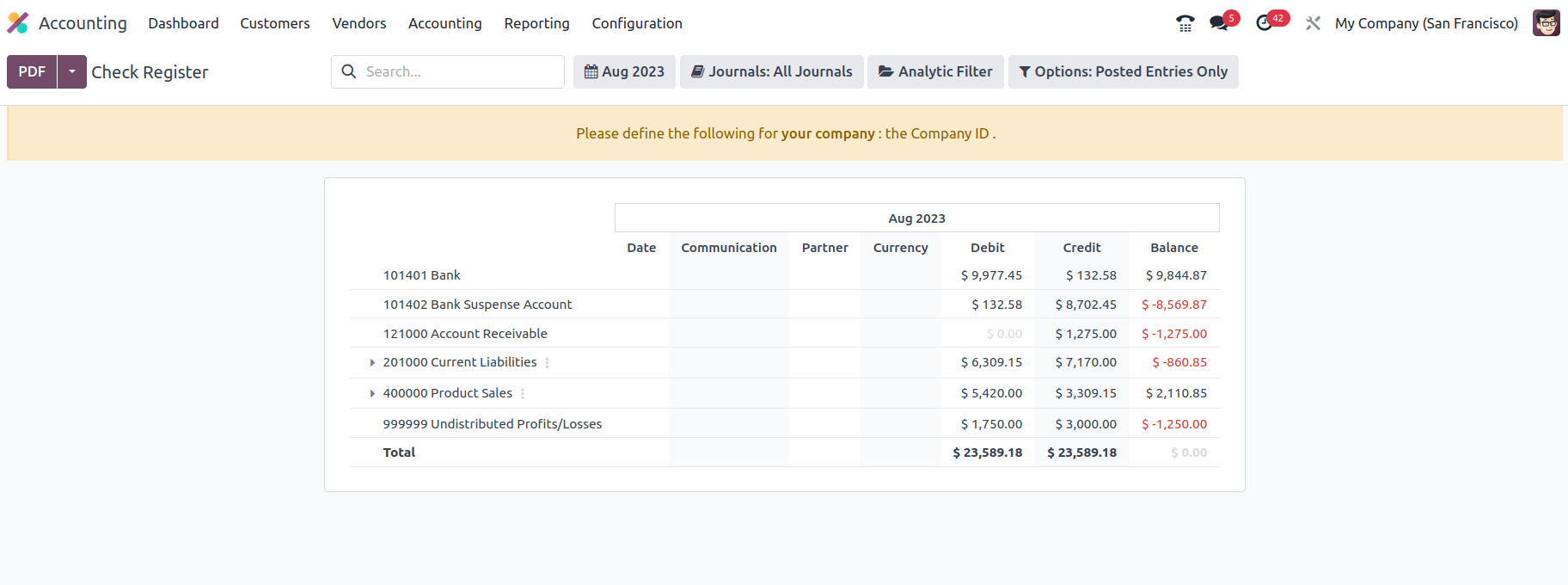
The Check Register reporting menu in Odoo will play an important part in carrying out each operation's elements in terms of the company's financial management and will be a valuable accounting tool. The Bill Register completes the reporting functions of the Odoo Accounting module.
Accounting and Business Administration-Advanced Certificate
designed to provide the learners with the required knowledge and hands-on skills needed to compete in the job market.